This is a shortcut for supplying the limits argument to the individual
scales. By default, any values outside the limits specified are replaced with
NA. Be warned that this will remove data outside the limits and this can
produce unintended results. For changing x or y axis limits without
dropping data observations, see coord_cartesian().
lims(...) xlim(...) ylim(...)
Arguments
| ... | For For |
|---|
See also
To expand the range of a plot to always include
certain values, see expand_limits(). For other types of data, see
scale_x_discrete(), scale_x_continuous(), scale_x_date().
Examples
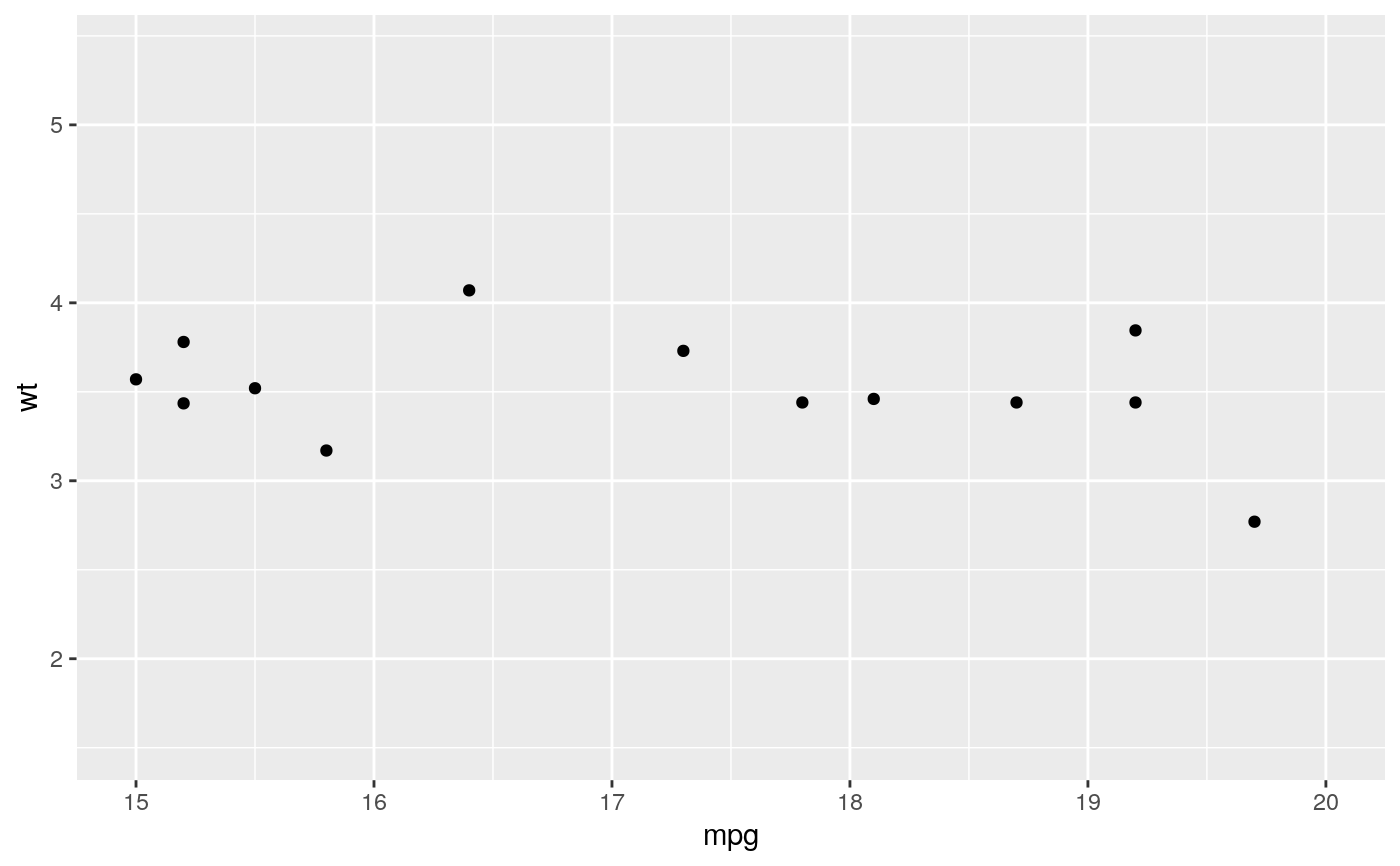
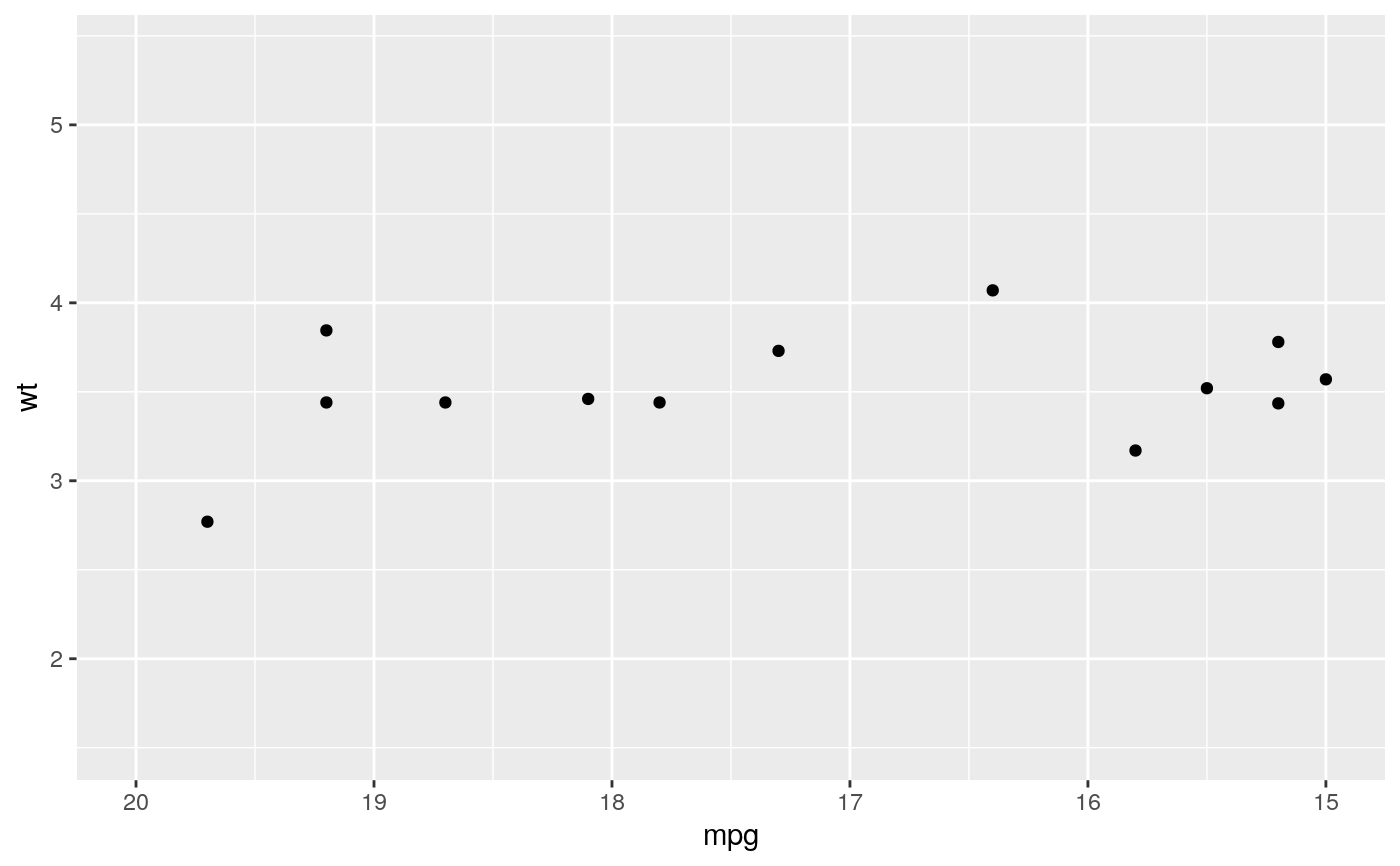
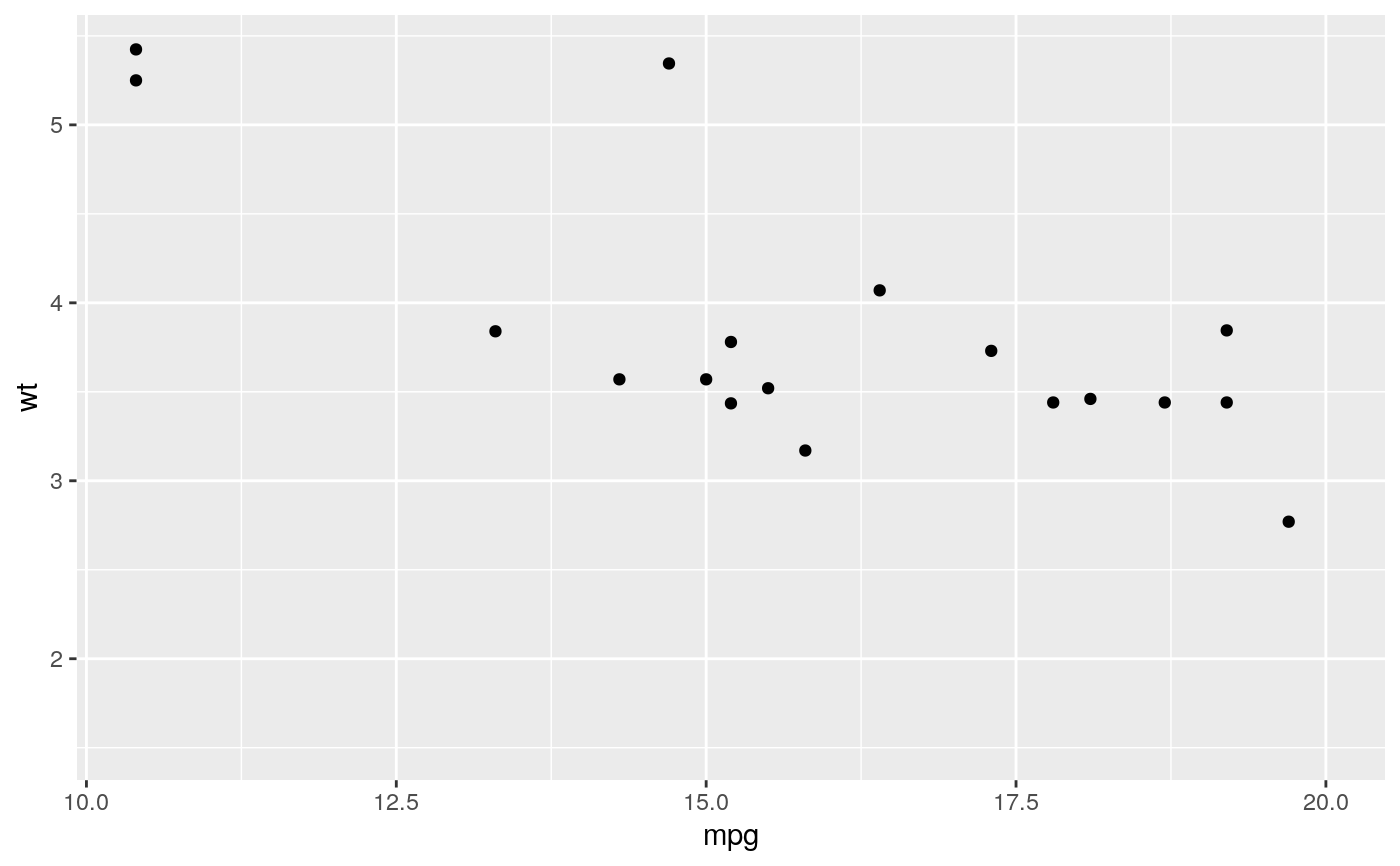
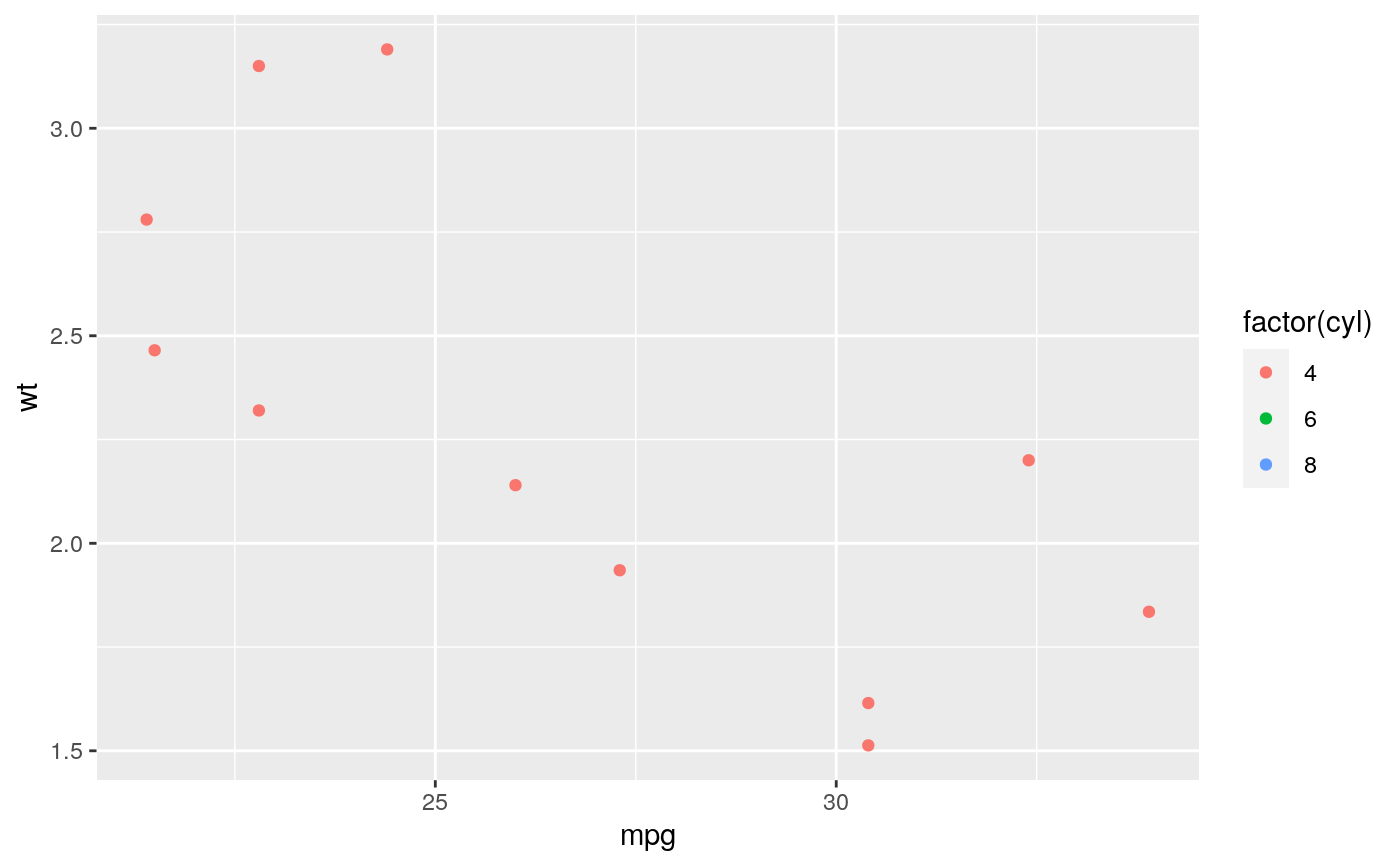
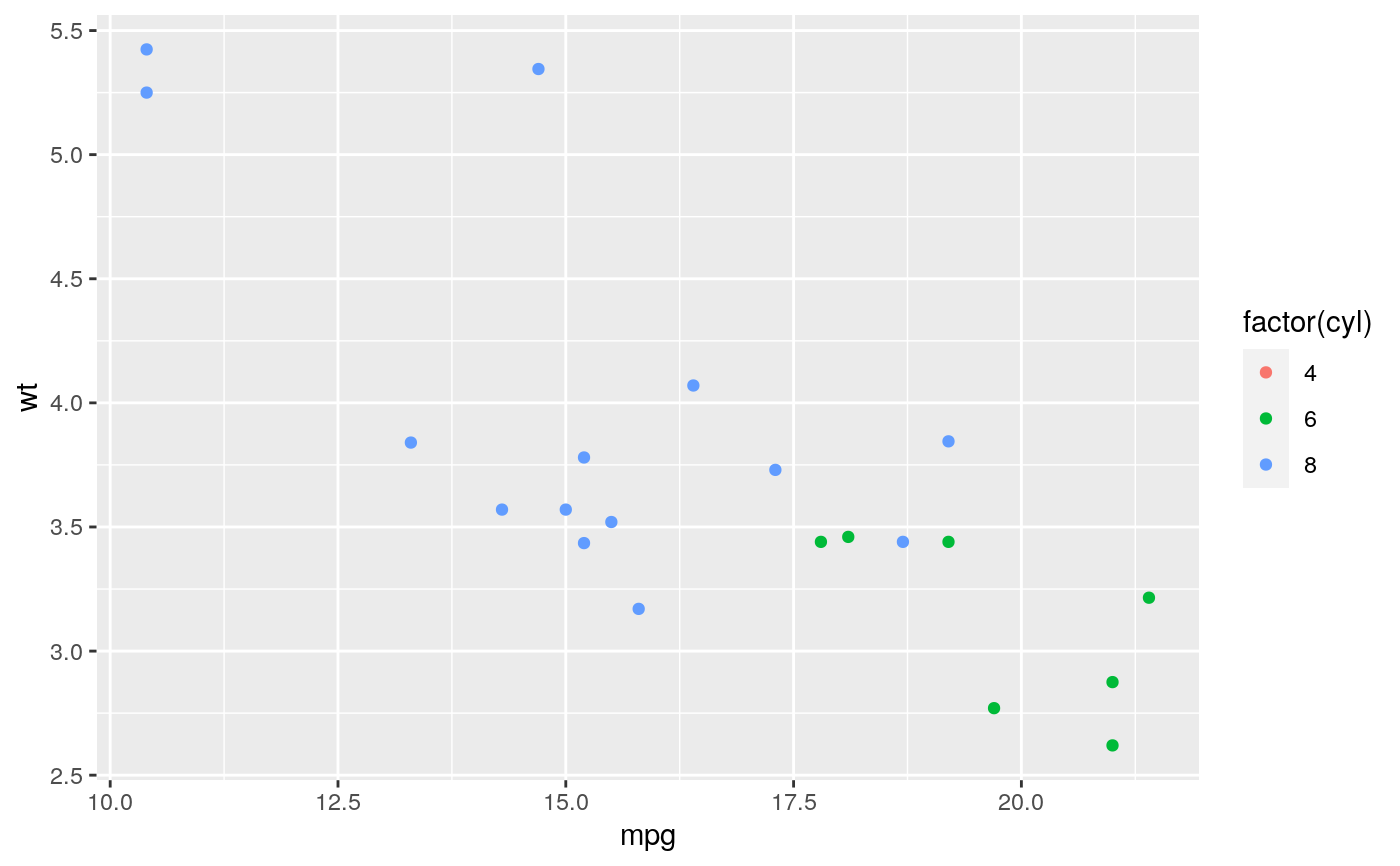
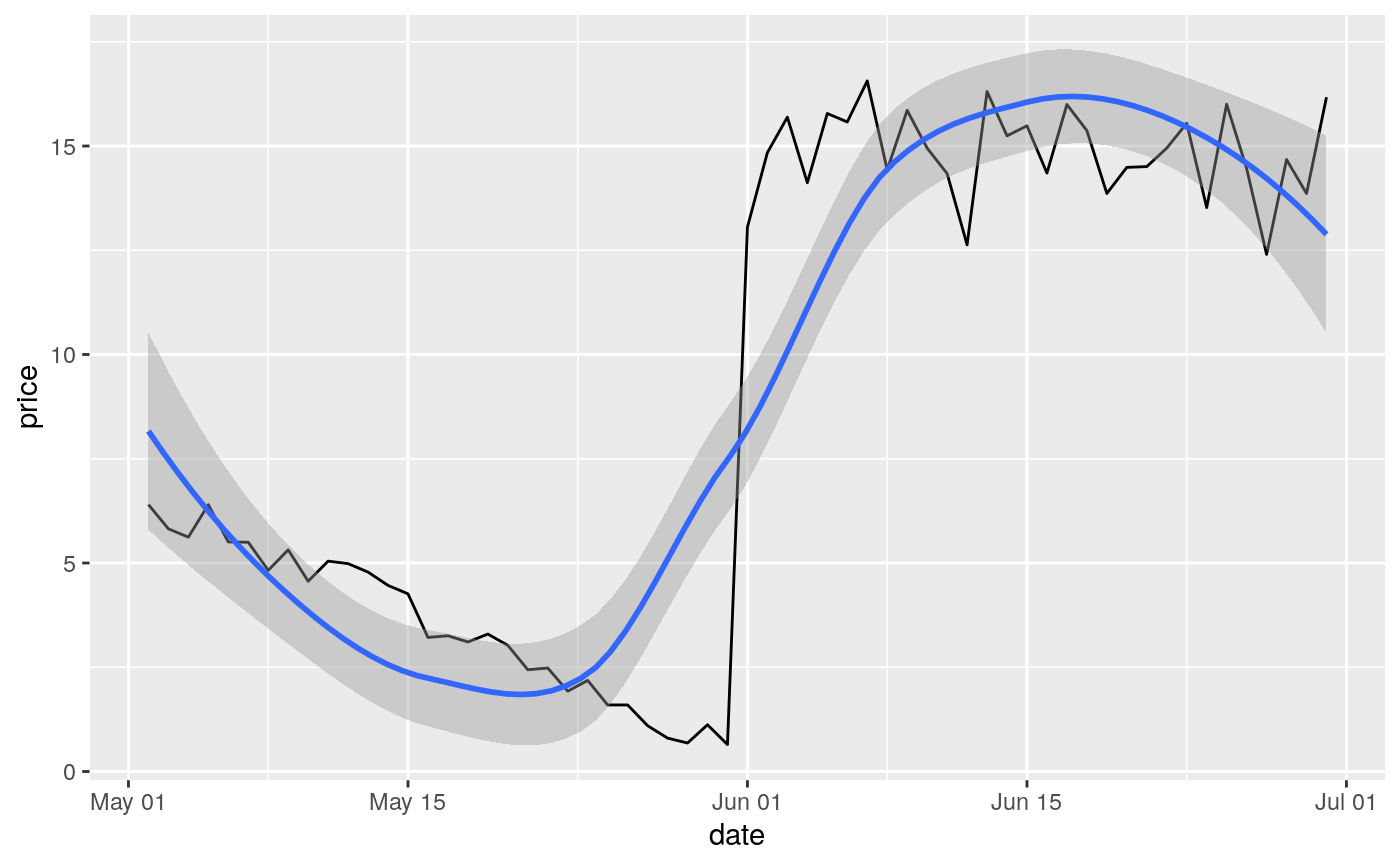
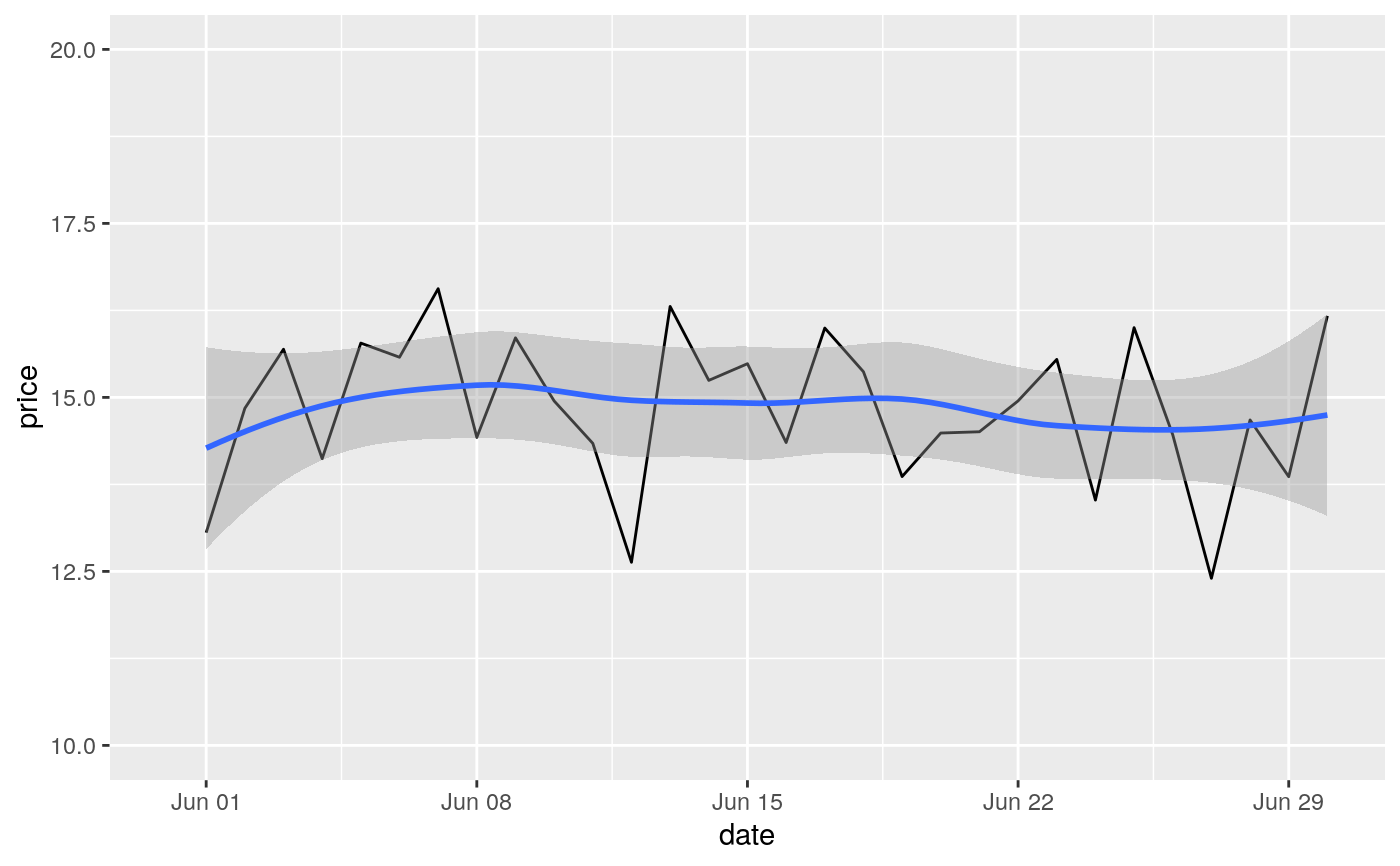
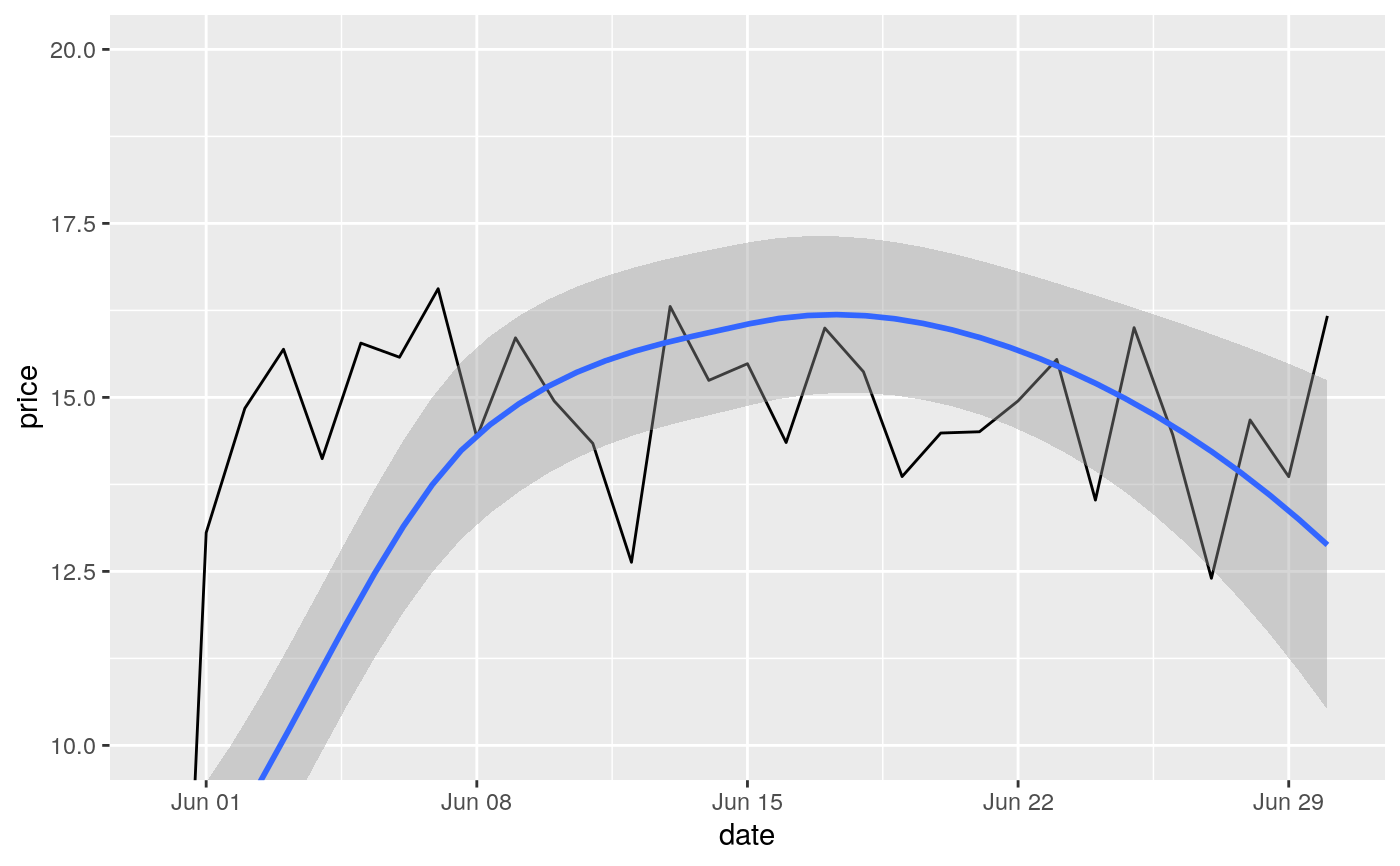
#> Warning: Removed 19 rows containing missing values (geom_point).#> Warning: Removed 19 rows containing missing values (geom_point).#> Warning: Removed 14 rows containing missing values (geom_point).# You can also supply limits that are larger than the data. # This is useful if you want to match scales across different plots small <- subset(mtcars, cyl == 4) big <- subset(mtcars, cyl > 4) ggplot(small, aes(mpg, wt, colour = factor(cyl))) + geom_point() + lims(colour = c("4", "6", "8"))# There are two ways of setting the axis limits: with limits or # with coordinate systems. They work in two rather different ways. last_month <- Sys.Date() - 0:59 df <- data.frame( date = last_month, price = c(rnorm(30, mean = 15), runif(30) + 0.2 * (1:30)) ) p <- ggplot(df, aes(date, price)) + geom_line() + stat_smooth() p#># Setting the limits with the scale discards all data outside the range. p + lims(x= c(Sys.Date() - 30, NA), y = c(10, 20))#>#> Warning: Removed 30 rows containing non-finite values (stat_smooth).#> Warning: Removed 30 row(s) containing missing values (geom_path).# For changing x or y axis limits **without** dropping data # observations use [coord_cartesian()]. Setting the limits on the # coordinate system performs a visual zoom. p + coord_cartesian(xlim =c(Sys.Date() - 30, NA), ylim = c(10, 20))#>