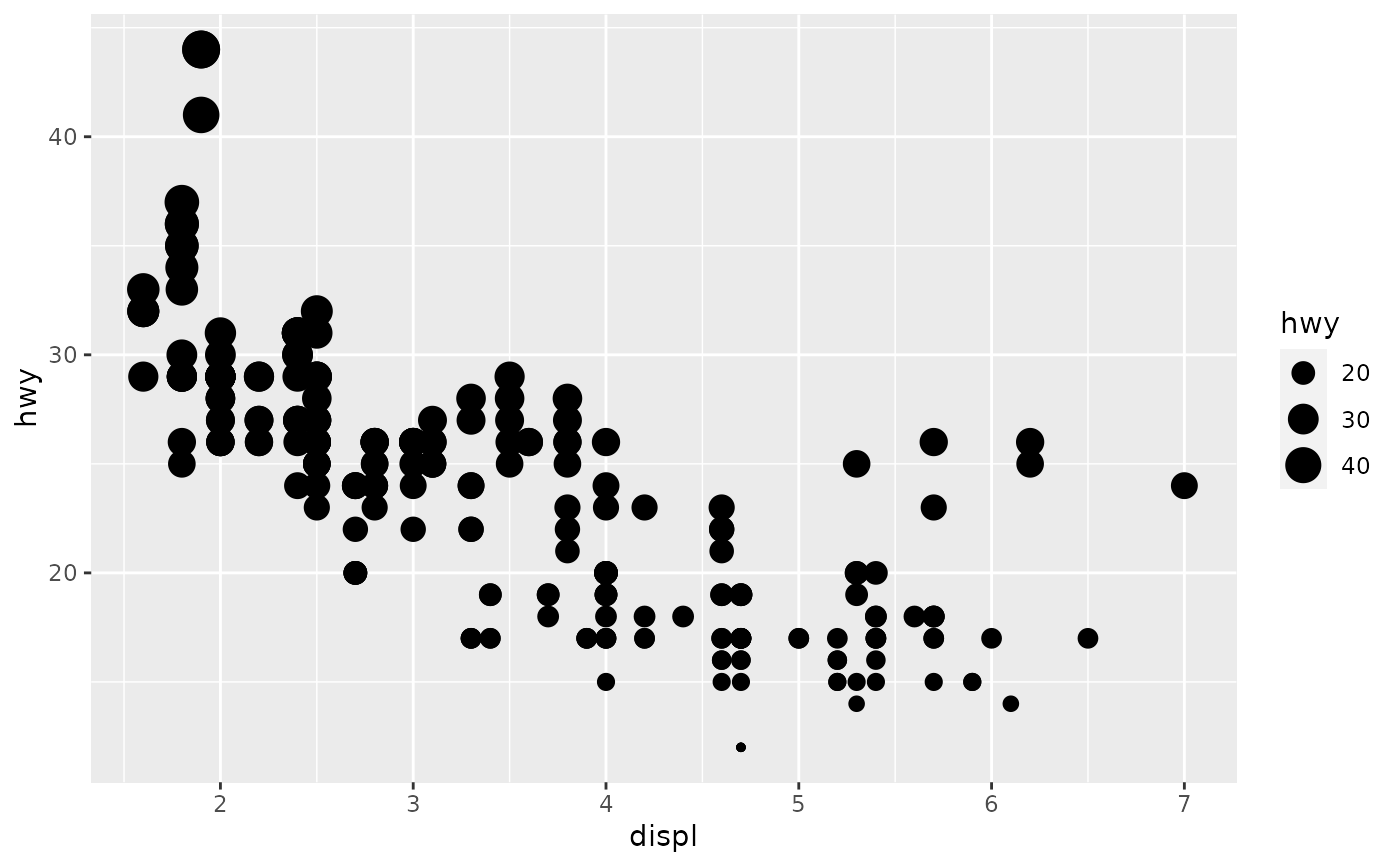
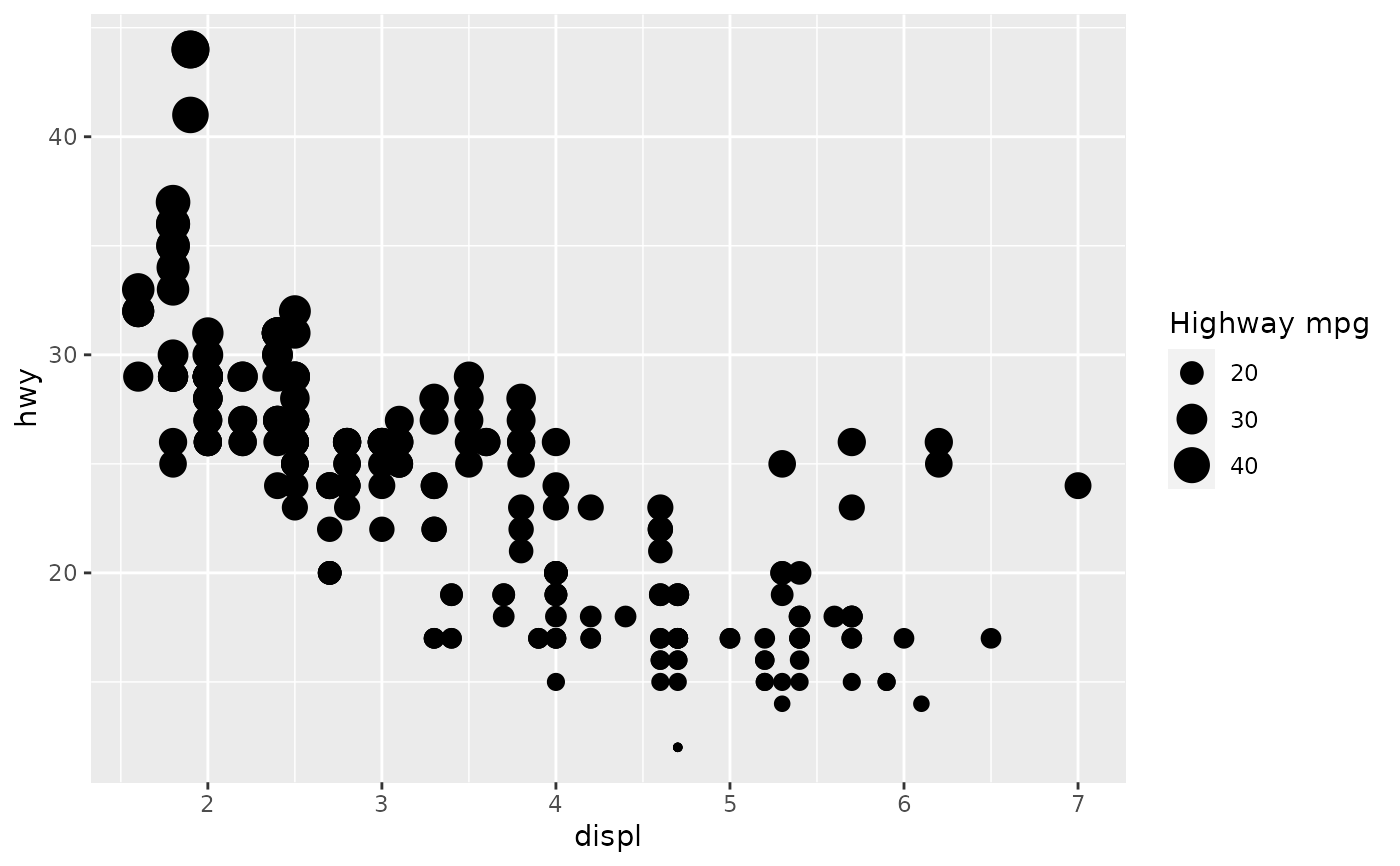
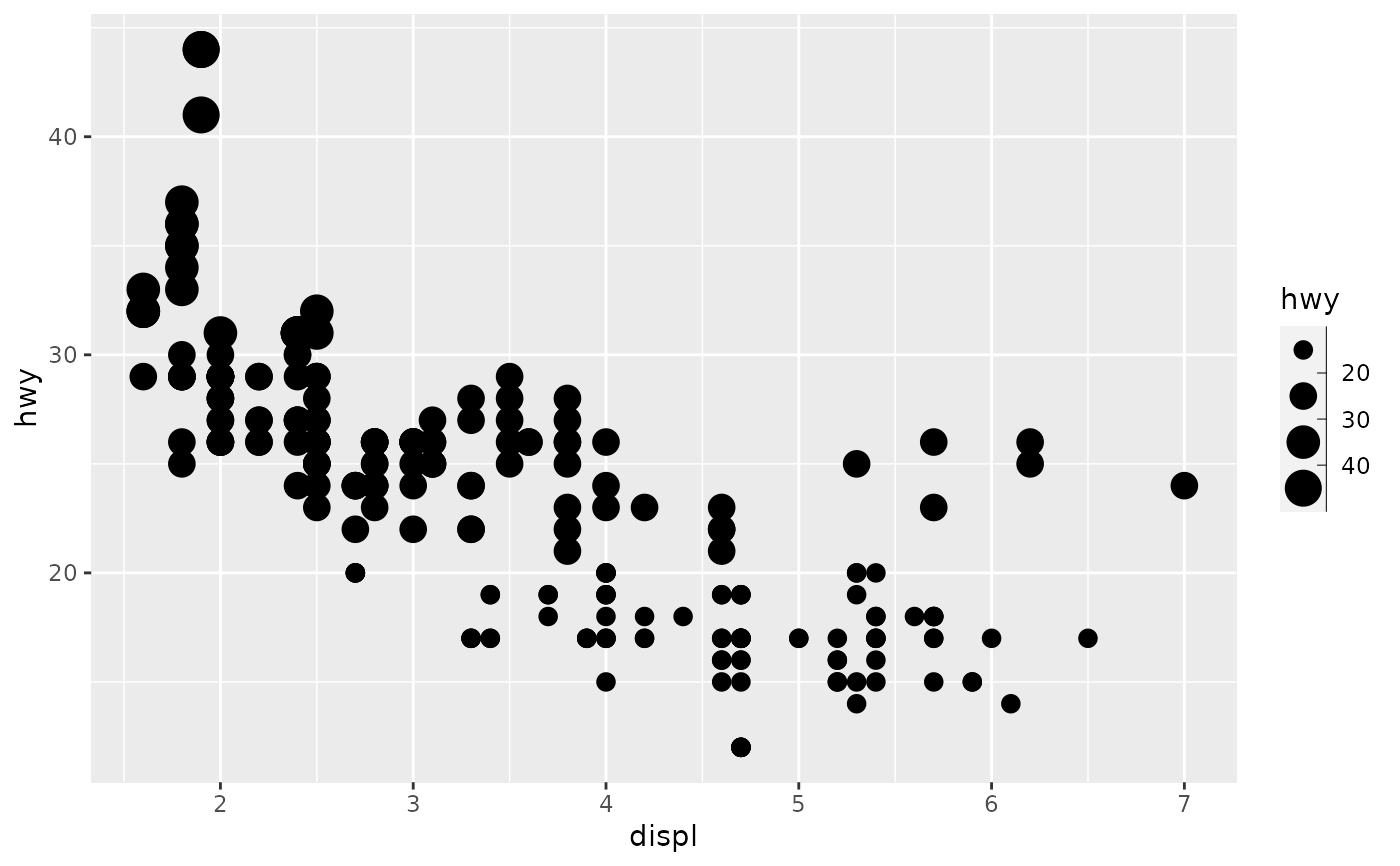
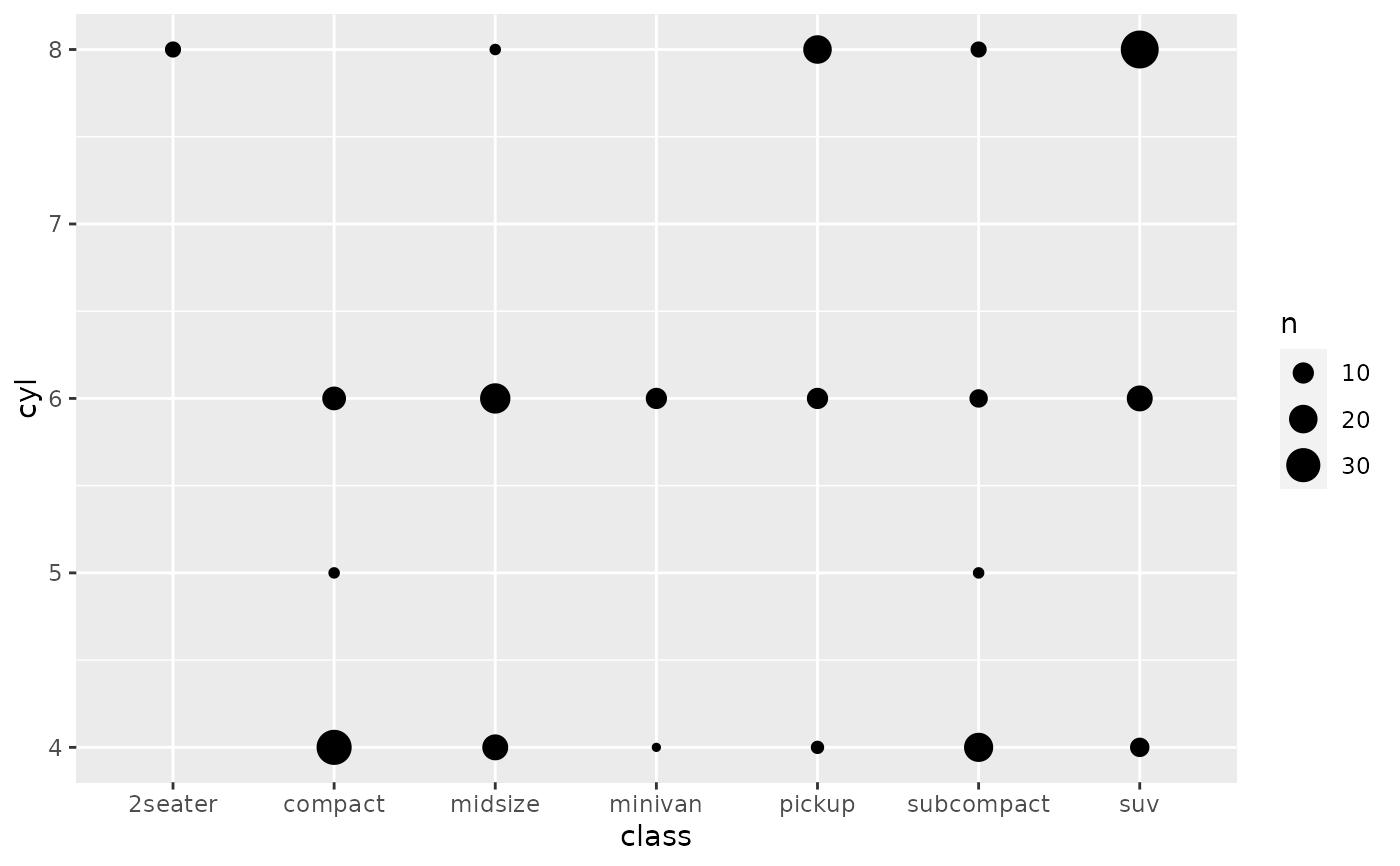
scale_size() scales area, scale_radius() scales radius. The size
aesthetic is most commonly used for points and text, and humans perceive
the area of points (not their radius), so this provides for optimal
perception. scale_size_area() ensures that a value of 0 is mapped
to a size of 0. scale_size_binned() is a binned version of scale_size() that
scales by area (but does not ensure 0 equals an area of zero). For a binned
equivalent of scale_size_area() use scale_size_binned_area().
scale_size( name = waiver(), breaks = waiver(), labels = waiver(), limits = NULL, range = c(1, 6), trans = "identity", guide = "legend" ) scale_radius( name = waiver(), breaks = waiver(), labels = waiver(), limits = NULL, range = c(1, 6), trans = "identity", guide = "legend" ) scale_size_binned( name = waiver(), breaks = waiver(), labels = waiver(), limits = NULL, range = c(1, 6), n.breaks = NULL, nice.breaks = TRUE, trans = "identity", guide = "bins" ) scale_size_area(..., max_size = 6) scale_size_binned_area(..., max_size = 6)
Arguments
| name | The name of the scale. Used as the axis or legend title. If
|
|---|---|
| breaks | One of:
|
| labels | One of: |
| limits | One of:
|
| range | a numeric vector of length 2 that specifies the minimum and maximum size of the plotting symbol after transformation. |
| trans | For continuous scales, the name of a transformation object or the object itself. Built-in transformations include "asn", "atanh", "boxcox", "date", "exp", "hms", "identity", "log", "log10", "log1p", "log2", "logit", "modulus", "probability", "probit", "pseudo_log", "reciprocal", "reverse", "sqrt" and "time". A transformation object bundles together a transform, its inverse,
and methods for generating breaks and labels. Transformation objects
are defined in the scales package, and are called |
| guide | A function used to create a guide or its name. See
|
| n.breaks | An integer guiding the number of major breaks. The algorithm
may choose a slightly different number to ensure nice break labels. Will
only have an effect if |
| nice.breaks | Logical. Should breaks be attempted placed at nice values
instead of exactly evenly spaced between the limits. If |
| ... | Arguments passed on to
|
| max_size | Size of largest points. |
See also
scale_size_area() if you want 0 values to be mapped
to points with size 0.
Examples
p + scale_size("Highway mpg")# If you want zero value to have zero size, use scale_size_area: p + scale_size_area()# Binning can sometimes make it easier to match the scaled data to the legend p + scale_size_binned()# This is most useful when size is a count ggplot(mpg, aes(class, cyl)) + geom_count() + scale_size_area()# If you want to map size to radius (usually bad idea), use scale_radius p + scale_radius()