+ is the key to constructing sophisticated ggplot2 graphics. It
allows you to start simple, then get more and more complex, checking your
work at each step.
# S3 method for gg
+(e1, e2)
e1 %+% e2What can you add?
You can add any of the following types of objects:
An
aes()object replaces the default aesthetics.A layer created by a
geom_orstat_function adds a new layer.A
scaleoverrides the existing scale.A
theme()modifies the current theme.A
coordoverrides the current coordinate system.A
facetspecification overrides the current faceting.
To replace the current default data frame, you must use %+%,
due to S3 method precedence issues.
You can also supply a list, in which case each element of the list will be added in turn.
See also
Examples
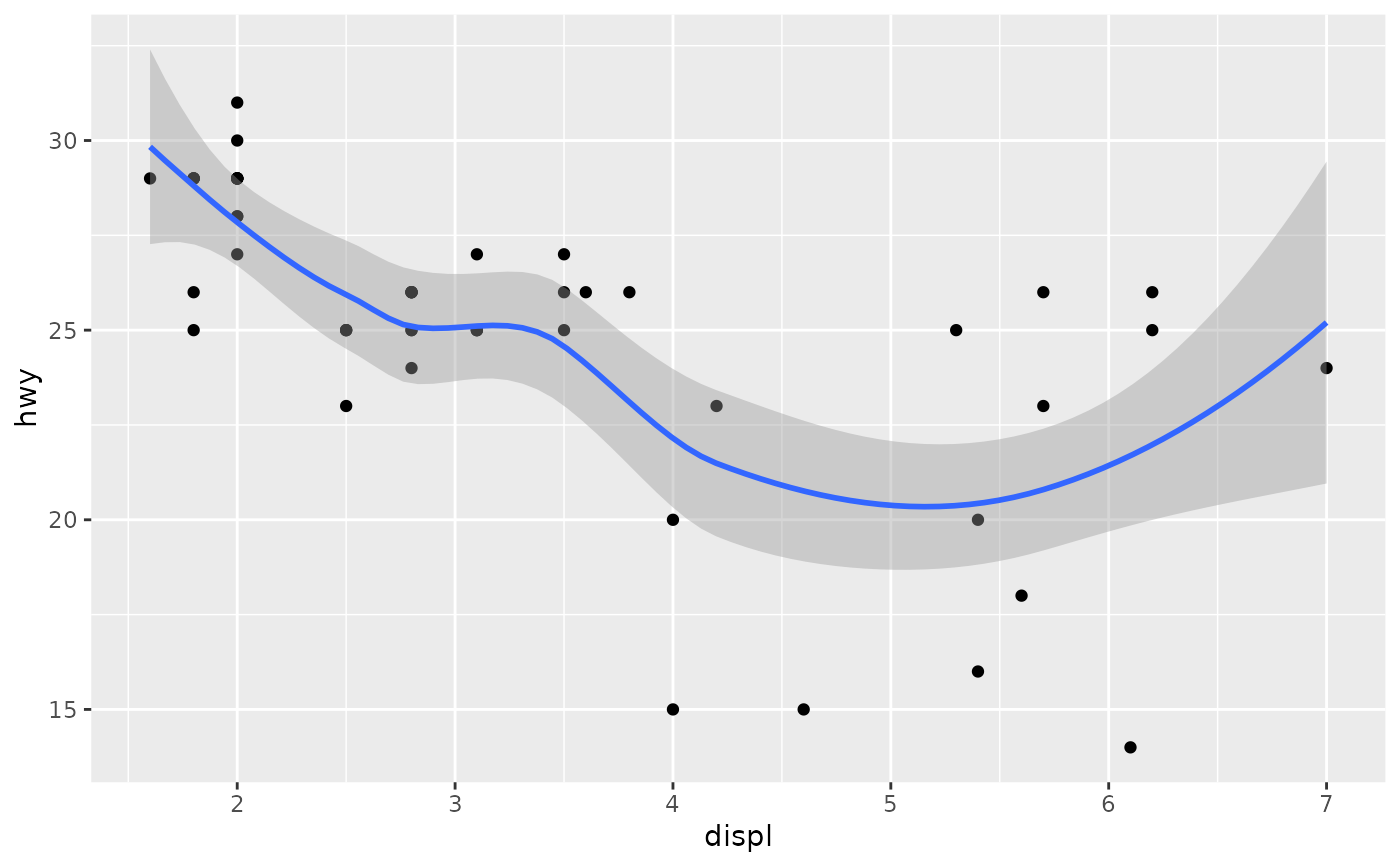
base <-
ggplot(mpg, aes(displ, hwy)) +
geom_point()
base + geom_smooth()
#> `geom_smooth()` using method = 'loess' and formula 'y ~ x'
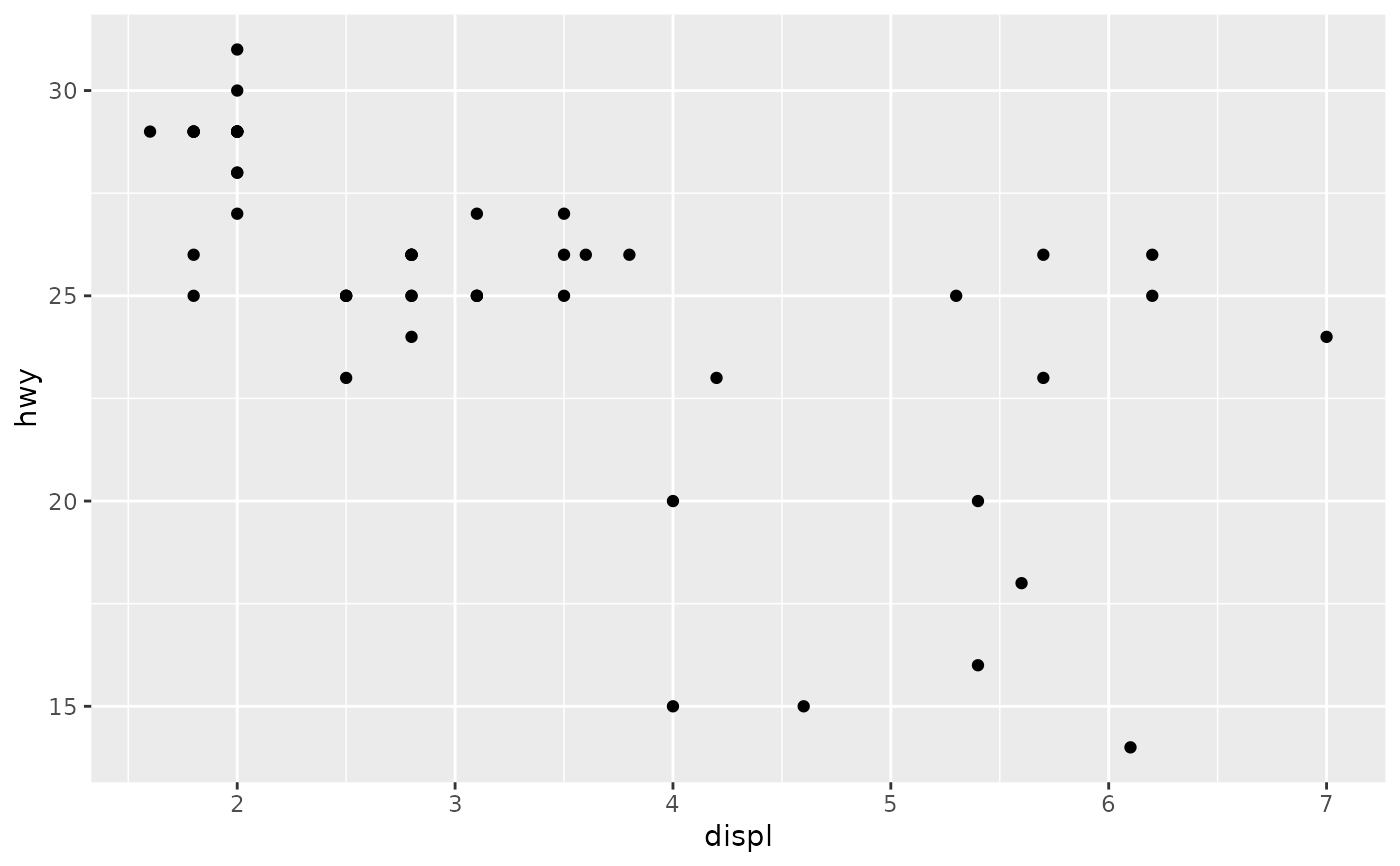
 # To override the data, you must use %+%
base %+% subset(mpg, fl == "p")
# To override the data, you must use %+%
base %+% subset(mpg, fl == "p")
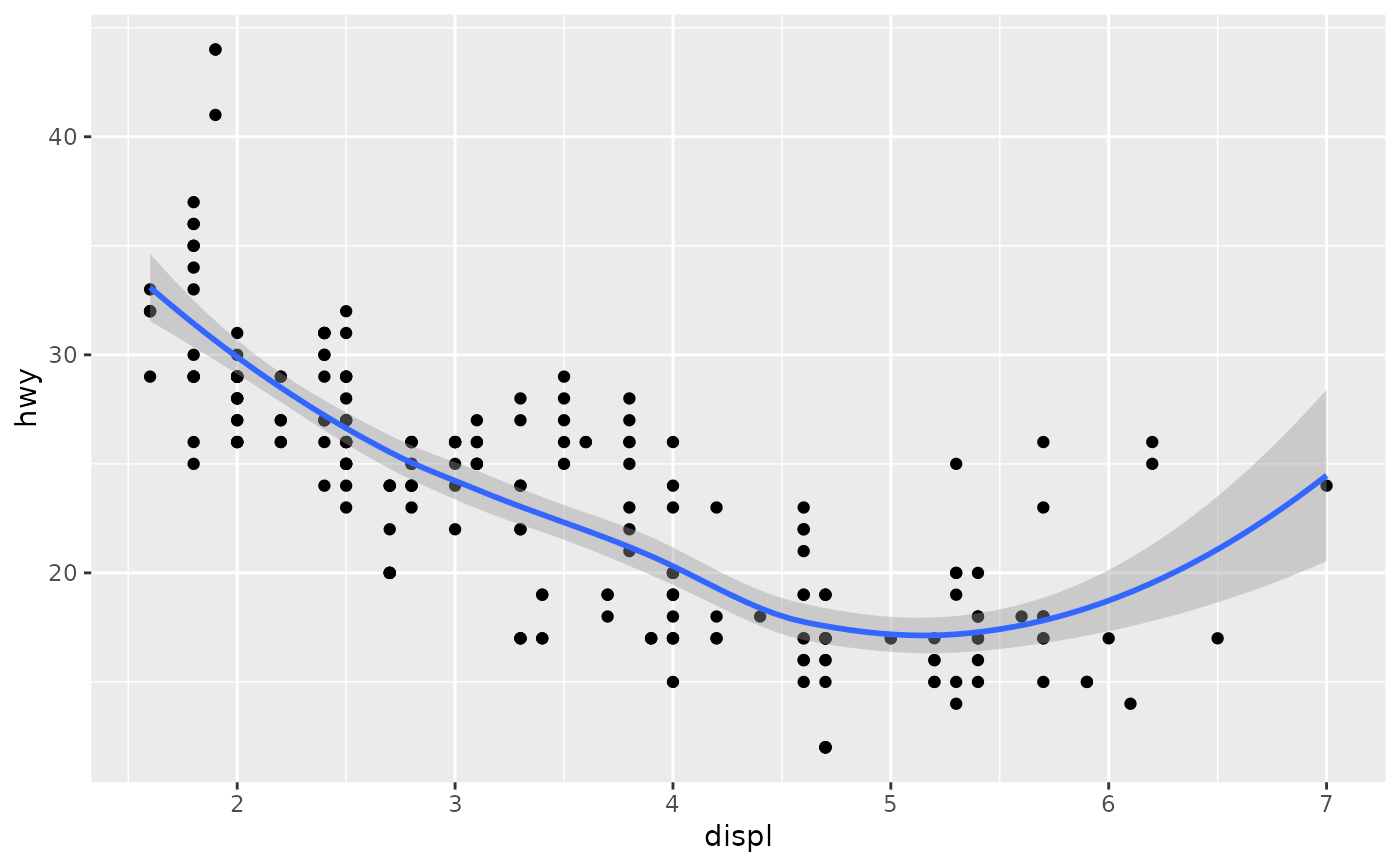
 # Alternatively, you can add multiple components with a list.
# This can be useful to return from a function.
base + list(subset(mpg, fl == "p"), geom_smooth())
#> `geom_smooth()` using method = 'loess' and formula 'y ~ x'
# Alternatively, you can add multiple components with a list.
# This can be useful to return from a function.
base + list(subset(mpg, fl == "p"), geom_smooth())
#> `geom_smooth()` using method = 'loess' and formula 'y ~ x'