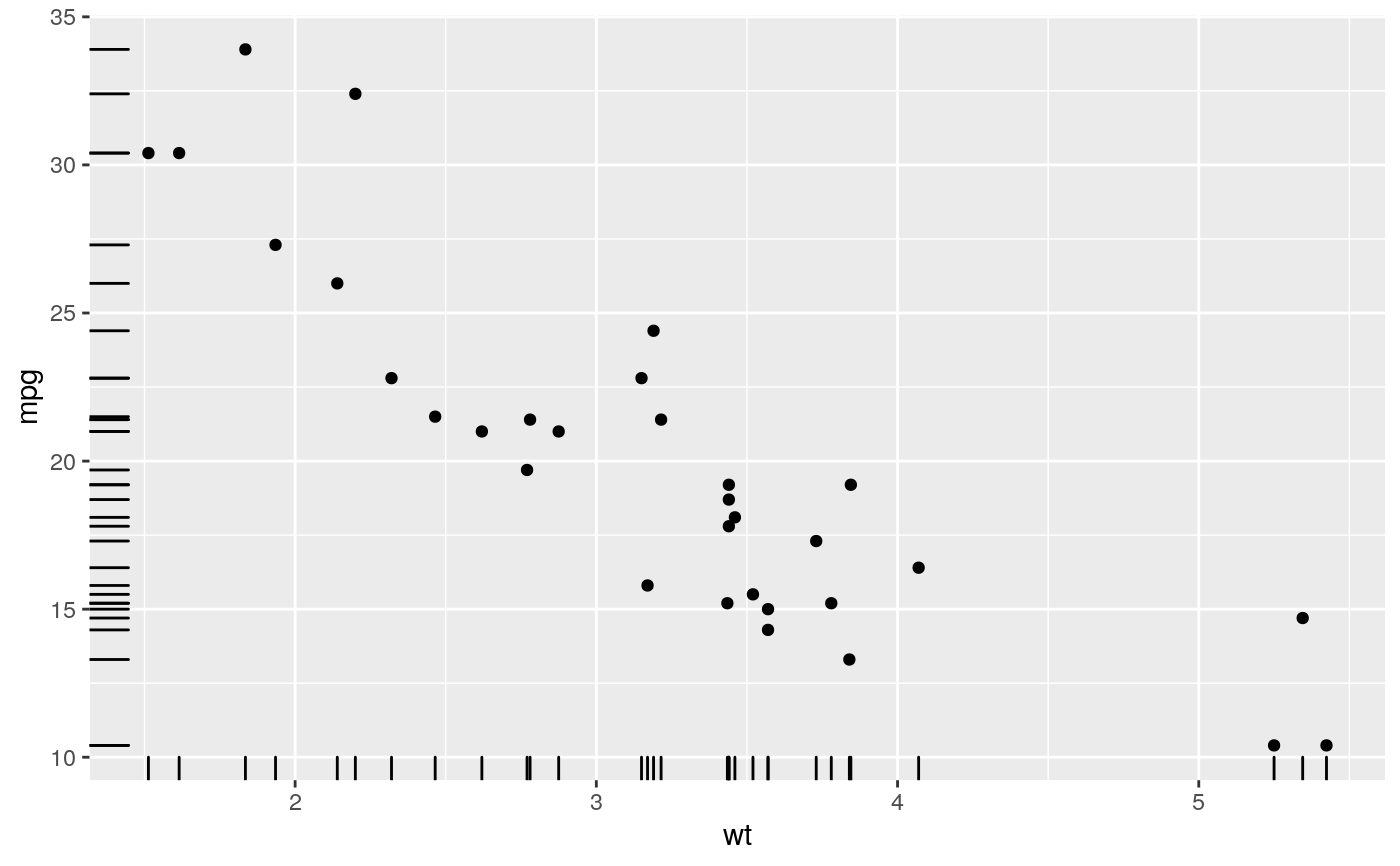
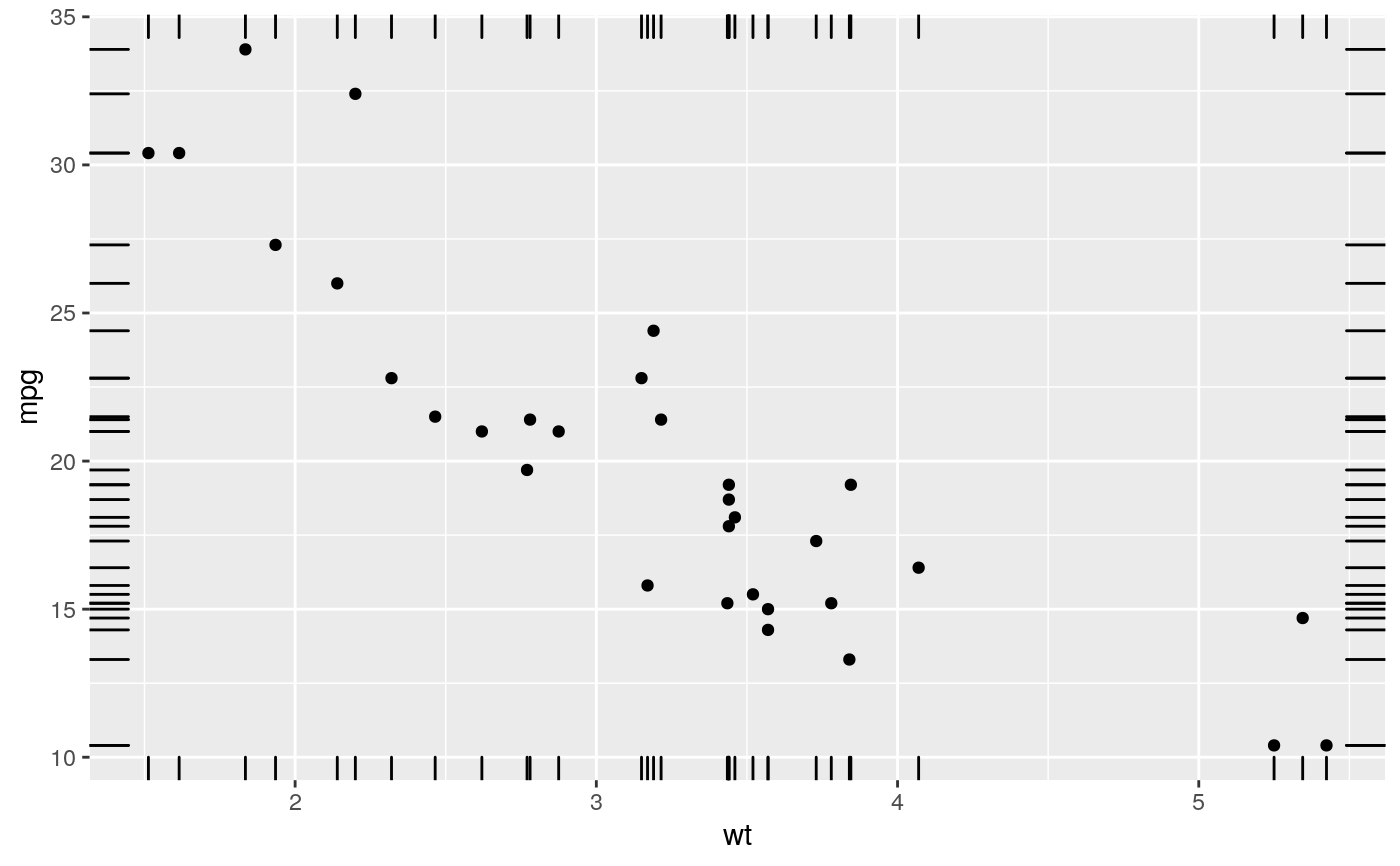
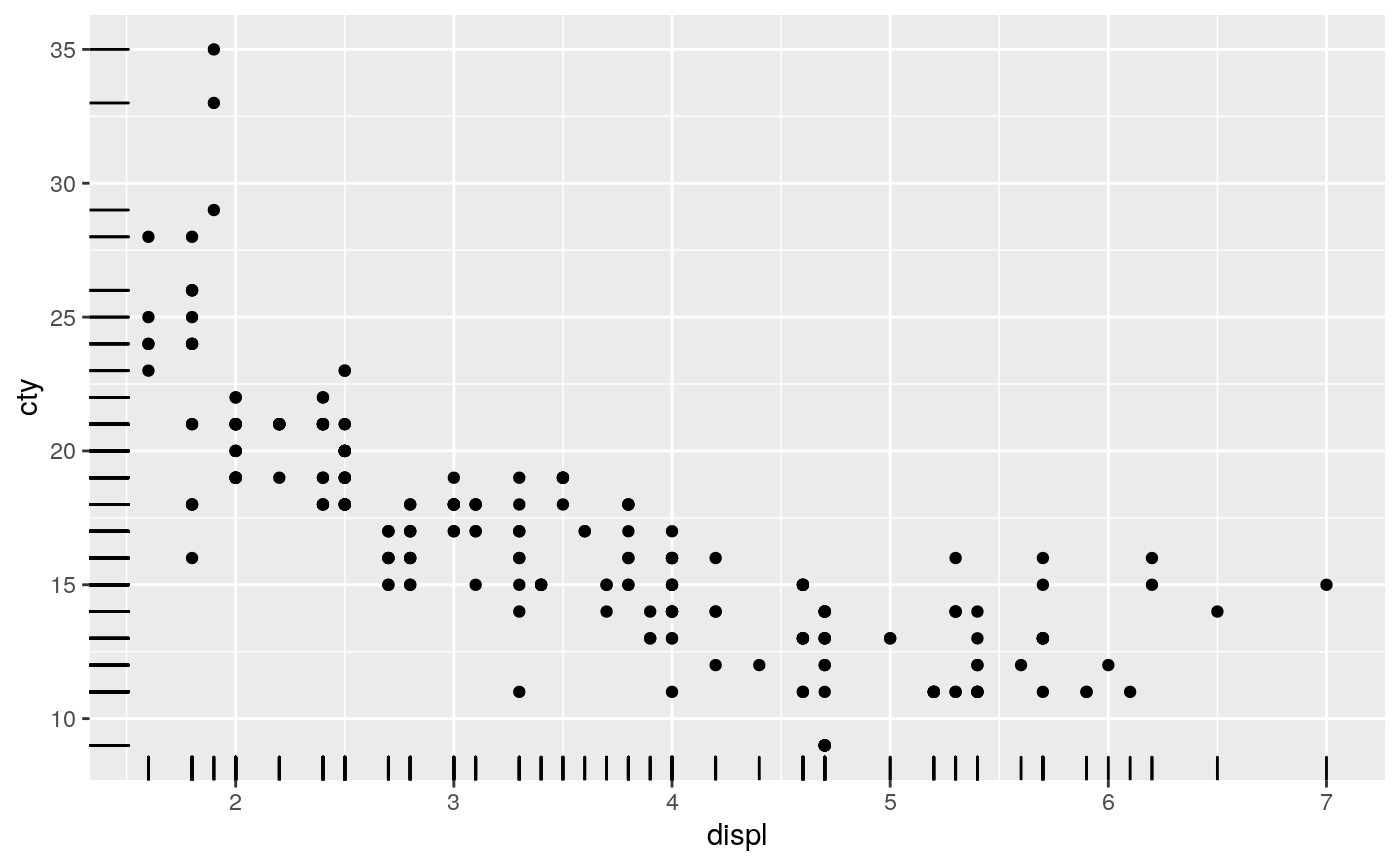
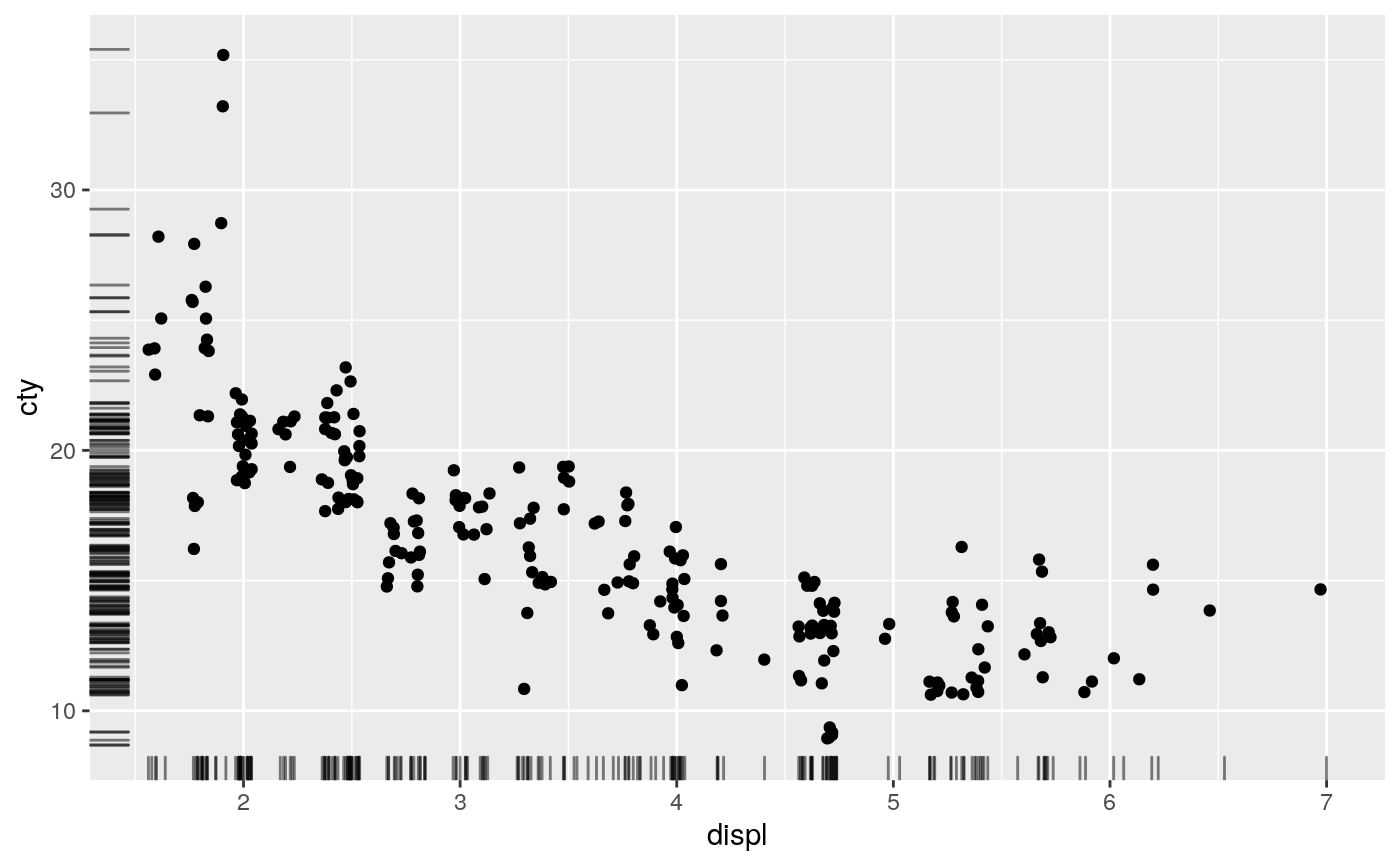
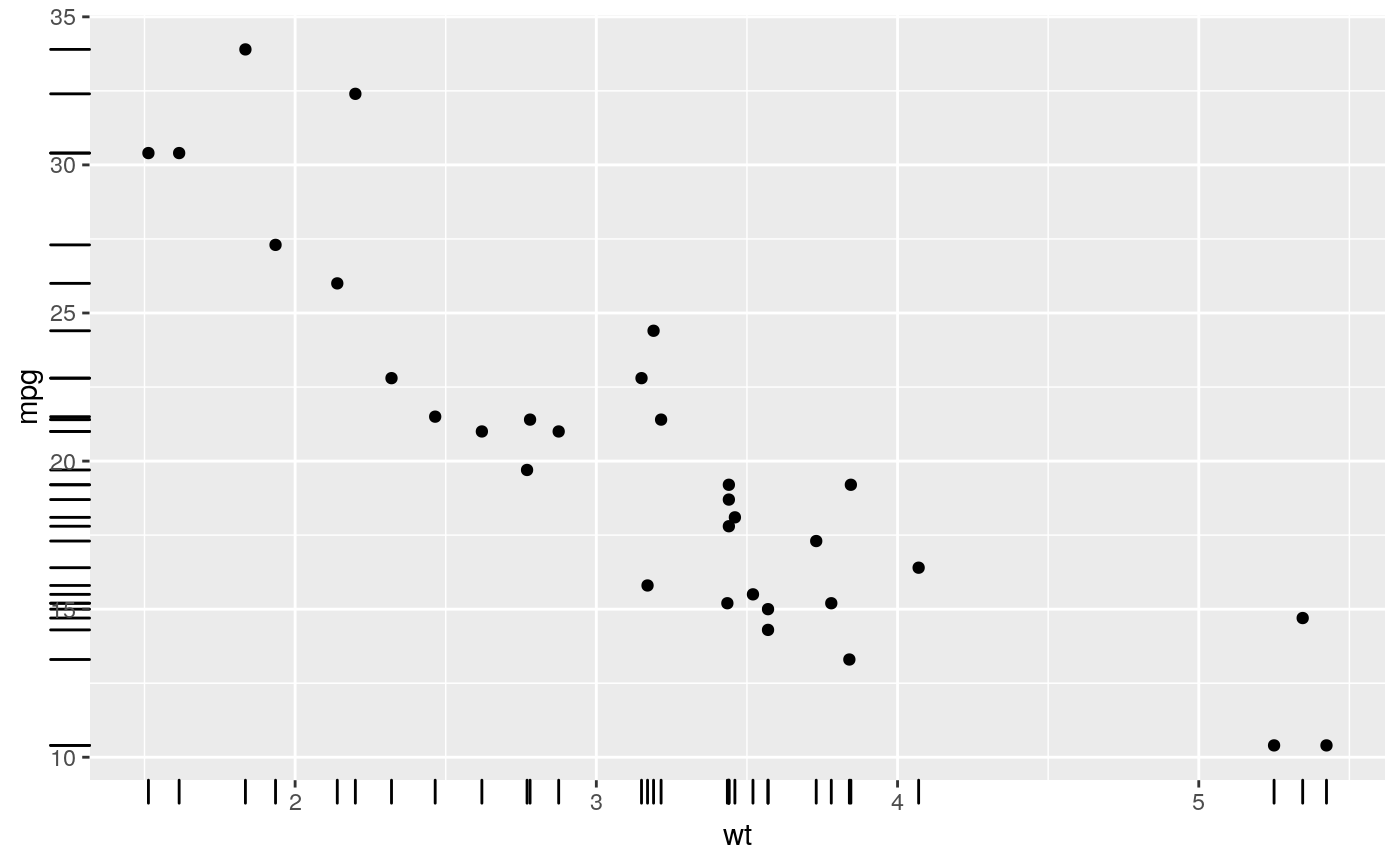
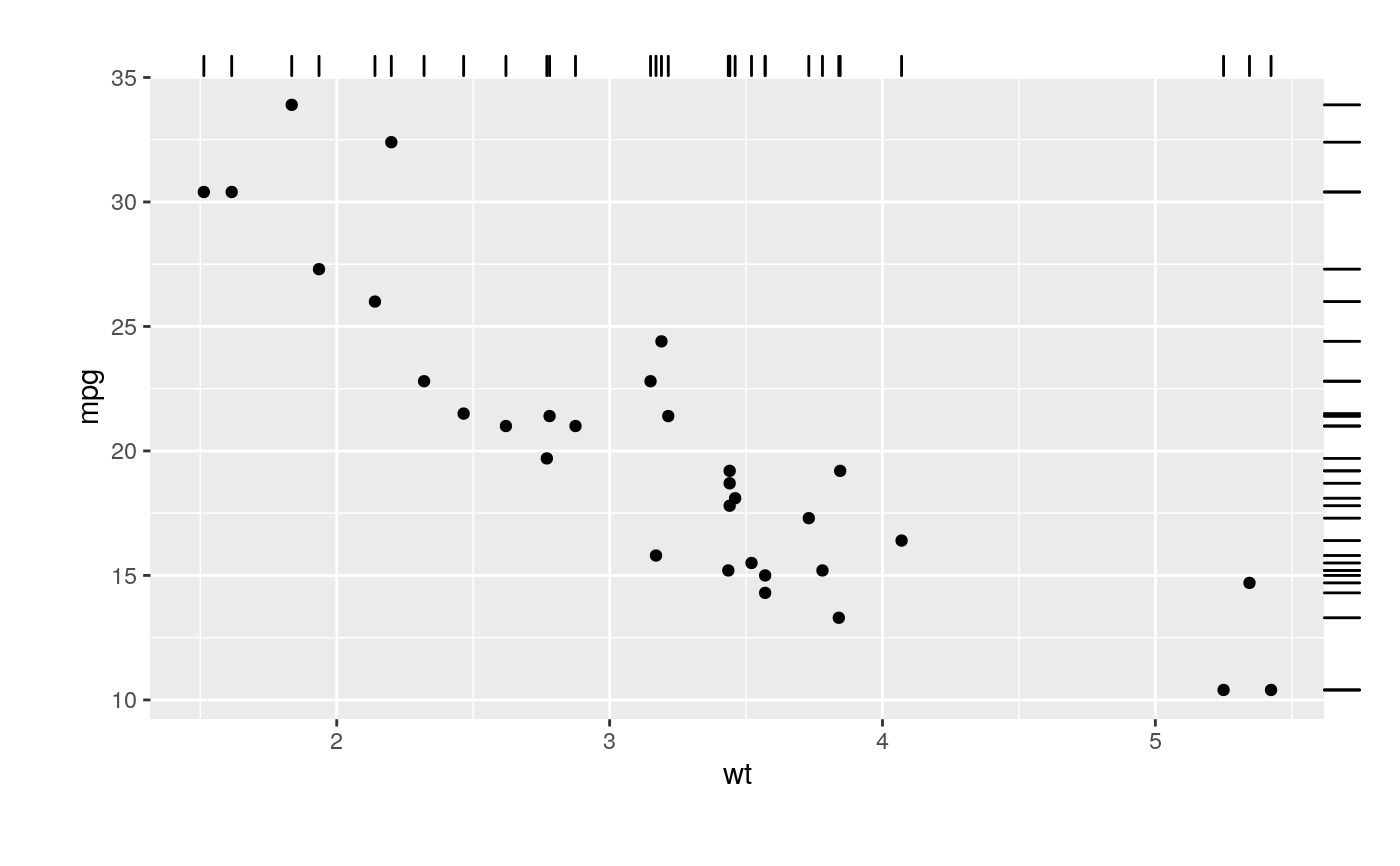
A rug plot is a compact visualisation designed to supplement a 2d display with the two 1d marginal distributions. Rug plots display individual cases so are best used with smaller datasets.
geom_rug( mapping = NULL, data = NULL, stat = "identity", position = "identity", ..., outside = FALSE, sides = "bl", length = unit(0.03, "npc"), na.rm = FALSE, show.legend = NA, inherit.aes = TRUE )
Arguments
| mapping | Set of aesthetic mappings created by |
|---|---|
| data | The data to be displayed in this layer. There are three options: If A A |
| stat | The statistical transformation to use on the data for this layer, as a string. |
| position | Position adjustment, either as a string, or the result of a call to a position adjustment function. |
| ... | Other arguments passed on to |
| outside | logical that controls whether to move the rug tassels outside of the plot area. Default is off (FALSE). You will also need to use |
| sides | A string that controls which sides of the plot the rugs appear on.
It can be set to a string containing any of |
| length | A |
| na.rm | If |
| show.legend | logical. Should this layer be included in the legends?
|
| inherit.aes | If |
Details
By default, the rug lines are drawn with a length that corresponds to 3% of the total plot size. Since the default scale expansion of for continuous variables is 5% at both ends of the scale, the rug will not overlap with any data points under the default settings.
Aesthetics
geom_rug() understands the following aesthetics (required aesthetics are in bold):
alphacolourgrouplinetypesizexy
Learn more about setting these aesthetics in vignette("ggplot2-specs").
Examples
p + geom_rug()p + geom_rug(sides="b") # Rug on bottom onlyp + geom_rug(sides="trbl") # All four sides# Use jittering to avoid overplotting for smaller datasets ggplot(mpg, aes(displ, cty)) + geom_point() + geom_rug()# move the rug tassels to outside the plot # remember to set clip = "off". p + geom_rug(outside = TRUE) + coord_cartesian(clip = "off")# set sides to top right, and then move the margins p + geom_rug(outside = TRUE, sides = "tr") + coord_cartesian(clip = "off") + theme(plot.margin = margin(1, 1, 1, 1, "cm"))# increase the line length and # expand axis to avoid overplotting p + geom_rug(length = unit(0.05, "npc")) + scale_y_continuous(expand = c(0.1, 0.1))