Create a row group with a collection of rows. This requires specification of
the rows to be included, either by supplying row labels, row indices, or
through use of a select helper function like starts_with().
tab_row_group(data, group = NULL, rows = NULL, others = NULL)
Arguments
| data | A table object that is created using the |
|---|---|
| group | The name of the row group. This text will also serve as the row group label. |
| rows | The rows to be made components of the row group. Can either be a
vector of row captions provided in |
| others | An option to set a default row group label for any rows not
formally placed in a row group named by |
Value
An object of class gt_tbl.
Figures
Function ID
2-4
See also
Other Create or Modify Parts:
tab_footnote(),
tab_header(),
tab_options(),
tab_source_note(),
tab_spanner_delim(),
tab_spanner(),
tab_stubhead(),
tab_style()
Examples
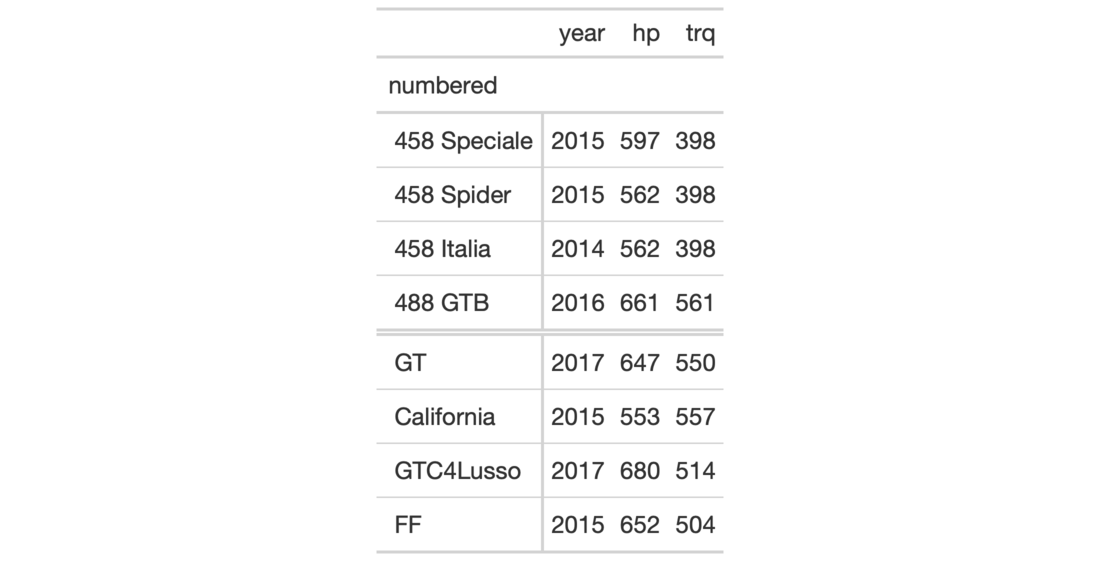
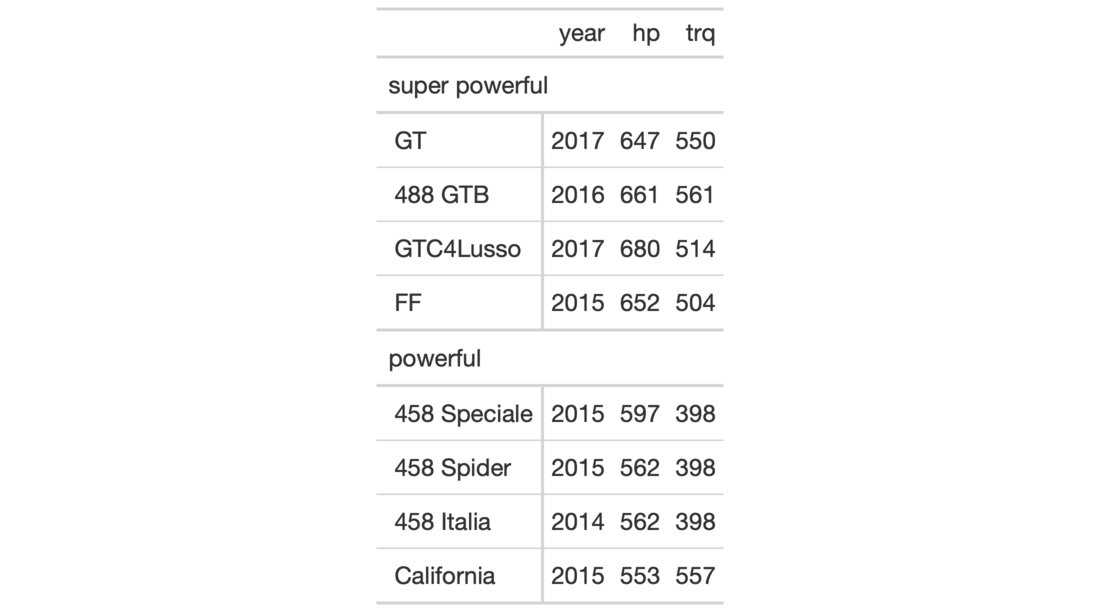
# Use `gtcars` to create a gt table and # add two row groups with the labels: # `numbered` and `NA` (a group without # a title, or, the rest) tab_1 <- gtcars %>% dplyr::select(model, year, hp, trq) %>% dplyr::slice(1:8) %>% gt(rowname_col = "model") %>% tab_row_group( group = "numbered", rows = matches("^[0-9]") ) # Use `gtcars` to create a gt table; # add two row groups with the labels # `powerful` and `super powerful`: the # distinction being `hp` lesser or # greater than `600` tab_2 <- gtcars %>% dplyr::select(model, year, hp, trq) %>% dplyr::slice(1:8) %>% gt(rowname_col = "model") %>% tab_row_group( group = "powerful", rows = hp <= 600 ) %>% tab_row_group( group = "super powerful", rows = hp > 600 )