With the tab_style() function we can target specific cells and apply styles
to them. This is best done in conjunction with the helper functions
cell_text(), cell_fill(), and cell_borders(). At present this function
is focused on the application of styles for HTML output only (as such, other
output formats will ignore all tab_style() calls). Using the aforementioned
helper functions, here are some of the styles we can apply:
the background color of the cell (
cell_fill():color)the cell's text color, font, and size (
cell_text():color,font,size)the text style (
cell_text():style), enabling the use of italics or oblique text.the text weight (
cell_text():weight), allowing the use of thin to bold text (the degree of choice is greater with variable fonts)the alignment and indentation of text (
cell_text():alignandindent)the cell borders (
cell_borders())
tab_style(data, style, locations)
Arguments
| data | A table object that is created using the |
|---|---|
| style | a vector of styles to use. The |
| locations | the cell or set of cells to be associated with the style.
Supplying any of the |
Value
An object of class gt_tbl.
Figures
Function ID
2-8
See also
cell_text(), cell_fill(), and cell_borders() as helpers for
defining custom styles and cells_body() as one of many useful helper
functions for targeting the locations to be styled.
Other Create or Modify Parts:
tab_footnote(),
tab_header(),
tab_options(),
tab_row_group(),
tab_source_note(),
tab_spanner_delim(),
tab_spanner(),
tab_stubhead()
Examples
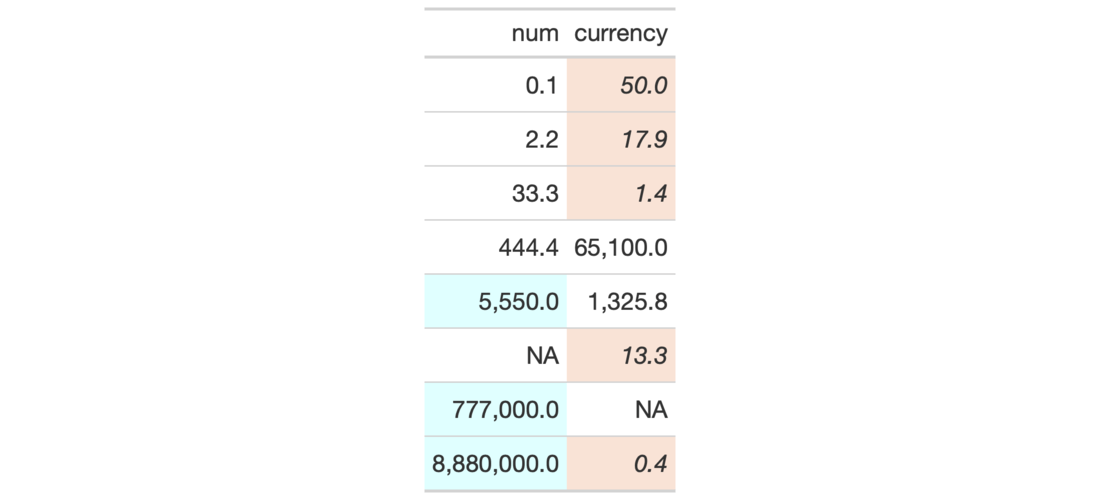
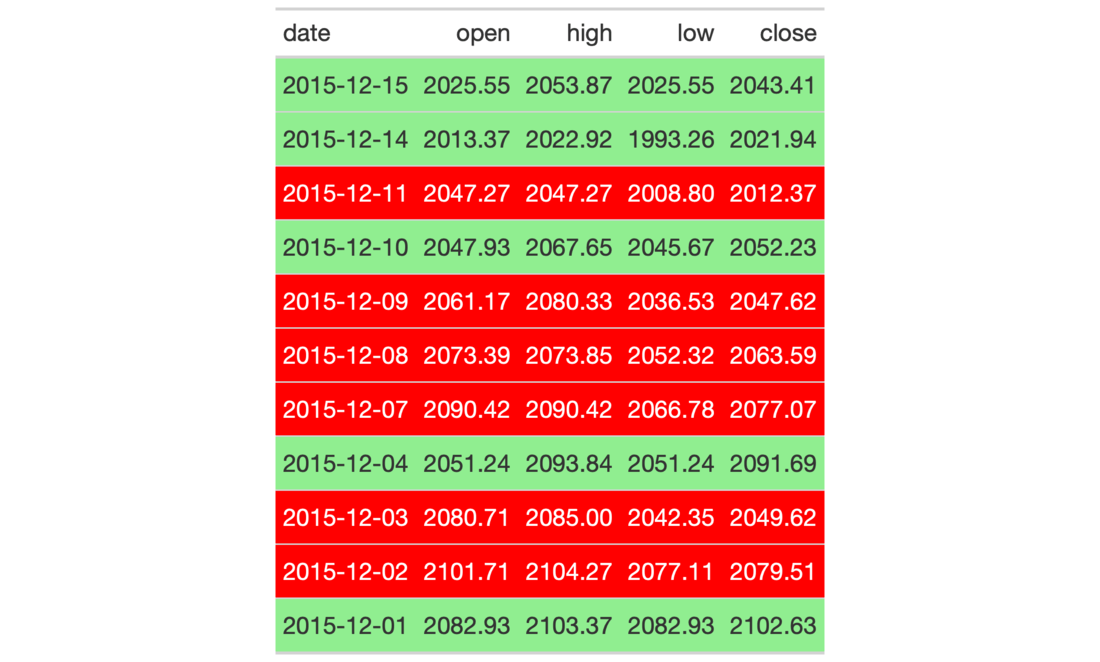
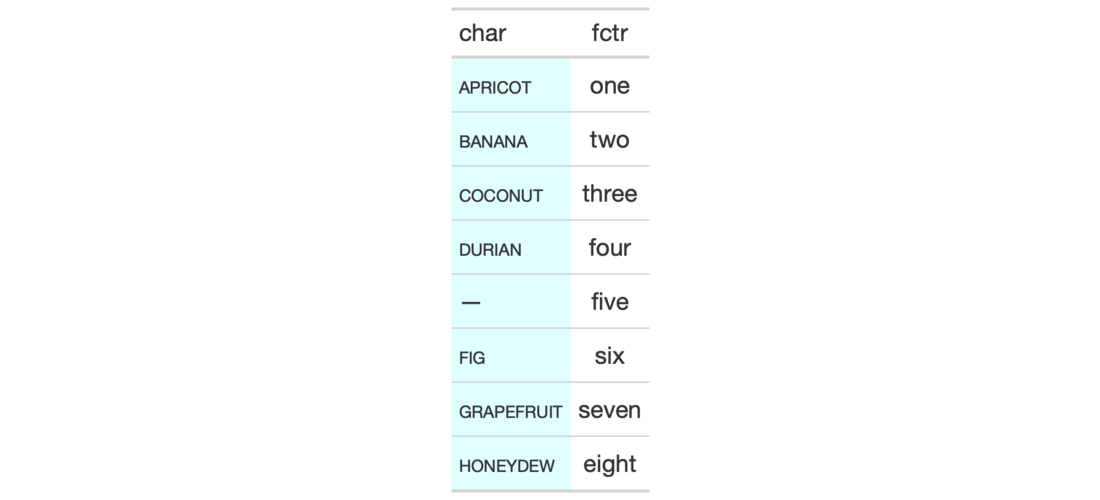
# Use `exibble` to create a gt table; # add styles that are to be applied # to data cells that satisfy a # condition (using `tab_style()`) tab_1 <- exibble %>% dplyr::select(num, currency) %>% gt() %>% fmt_number( columns = vars(num, currency), decimals = 1 ) %>% tab_style( style = list( cell_fill(color = "lightcyan"), cell_text(weight = "bold") ), locations = cells_body( columns = vars(num), rows = num >= 5000) ) %>% tab_style( style = list( cell_fill(color = "#F9E3D6"), cell_text(style = "italic") ), locations = cells_body( columns = vars(currency), rows = currency < 100) ) # Use `sp500` to create a gt table; # color entire rows of cells based # on values in a particular column tab_2 <- sp500 %>% dplyr::filter( date >= "2015-12-01" & date <= "2015-12-15" ) %>% dplyr::select(-c(adj_close, volume)) %>% gt() %>% tab_style( style = cell_fill(color = "lightgreen"), locations = cells_body( rows = close > open) ) %>% tab_style( style = list( cell_fill(color = "red"), cell_text(color = "white") ), locations = cells_body( rows = open > close) ) # Use `exibble` to create a gt table; # replace missing values with the # `fmt_missing()` function and then # add styling to the `char` column # with `cell_fill()` and with a # CSS style declaration tab_3 <- exibble %>% dplyr::select(char, fctr) %>% gt() %>% fmt_missing(everything()) %>% tab_style( style = list( cell_fill(color = "lightcyan"), "font-variant: small-caps;" ), locations = cells_body(columns = vars(char)) )