With numeric values in a gt table, we can perform formatting so that the targeted values are rendered in scientific notation. Furthermore, there is fine control with the following options:
decimals: choice of the number of decimal places, option to drop trailing zeros, and a choice of the decimal symbol
scaling: we can choose to scale targeted values by a multiplier value
pattern: option to use a text pattern for decoration of the formatted values
locale-based formatting: providing a locale ID will result in formatting specific to the chosen locale
fmt_scientific( data, columns, rows = NULL, decimals = 2, drop_trailing_zeros = FALSE, scale_by = 1, pattern = "{x}", sep_mark = ",", dec_mark = ".", locale = NULL )
Arguments
| data | A table object that is created using the |
|---|---|
| columns | The columns to format. Can either be a series of column names
provided in |
| rows | Optional rows to format. Not providing any value results in all
rows in |
| decimals | An option to specify the exact number of decimal places to
use. The default number of decimal places is |
| drop_trailing_zeros | A logical value that allows for removal of trailing zeros (those redundant zeros after the decimal mark). |
| scale_by | A value to scale the input. The default is |
| pattern | A formatting pattern that allows for decoration of the
formatted value. The value itself is represented by |
| sep_mark | The mark to use as a separator between groups of digits
(e.g., using |
| dec_mark | The character to use as a decimal mark (e.g., using |
| locale | An optional locale ID that can be used for formatting the value
according the locale's rules. Examples include |
Value
An object of class gt_tbl.
Details
Targeting of values is done through columns and additionally by rows (if
nothing is provided for rows then entire columns are selected). A number of
helper functions exist to make targeting more effective. Conditional
formatting is possible by providing a conditional expression to the rows
argument. See the Arguments section for more information on this.
Figures
Function ID
3-2
See also
Other Format Data:
data_color(),
fmt_currency(),
fmt_datetime(),
fmt_date(),
fmt_markdown(),
fmt_missing(),
fmt_number(),
fmt_passthrough(),
fmt_percent(),
fmt_time(),
fmt(),
text_transform()
Examples
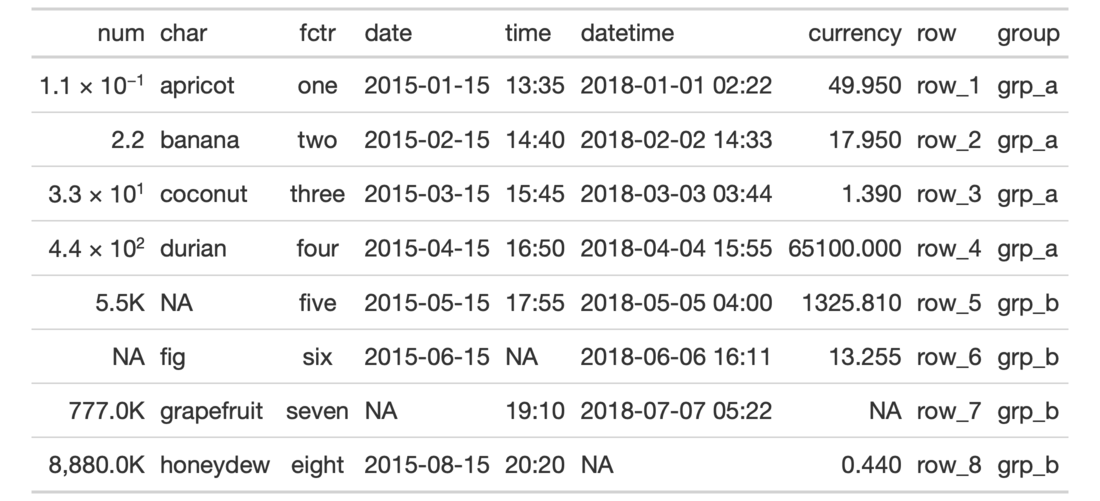
# Use `exibble` to create a gt table; # format the `num` column as partially # numeric and partially in scientific # notation tab_1 <- exibble %>% gt() %>% fmt_number( columns = vars(num), rows = num > 500, decimals = 1, scale_by = 1/1000, pattern = "{x}K" ) %>% fmt_scientific( columns = vars(num), rows = num <= 500, decimals = 1 )