The cells_stub_summary() function is used to target the stub cells of
summary and it is useful when applying a footnote with tab_footnote() or
adding custom styles with tab_style(). The function is expressly used in
each of those functions' locations argument. The 'stub_summary' location is
generated by the summary_rows() function.
cells_stub_summary(groups = everything(), rows = everything())
Arguments
| groups | The names of the groups that are to be targeted. |
|---|---|
| rows | The names of the rows that are to be targeted. |
Value
A list object with the classes cells_stub_summary and
location_cells.
Overview of Location Helper Functions
Location helper functions can be used to target cells with virtually any
function that has a locations argument. Here is a listing of all of the
location helper functions, with locations corresponding roughly from top to
bottom of a table:
cells_title(): targets the table title or the table subtitle depending on the value given to thegroupsargument ("title"or"subtitle").cells_stubhead(): targets the stubhead location, a cell of which is only available when there is a stub; a label in that location can be created by using thetab_stubhead()function.cells_column_spanners(): targets the spanner column labels with thespannersargument; spanner column labels appear above the column labels.cells_column_labels(): targets the column labels with itscolumnsargument.cells_row_groups(): targets the row group labels in any available row groups using thegroupsargument.cells_stub(): targets row labels in the table stub using therowsargument.cells_body(): targets data cells in the table body using intersections ofcolumnsandrows.cells_summary(): targets summary cells in the table body using thegroupsargument and intersections ofcolumnsandrows.cells_grand_summary(): targets cells of the table's grand summary using intersections ofcolumnsandrowscells_stub_summary(): targets summary row labels in the table stub using thegroupsandrowsarguments.cells_stub_grand_summary(): targets grand summary row labels in the table stub using therowsargument.cells_footnotes(): targets all footnotes in the table footer (cannot be used withtab_footnote()).cells_source_notes(): targets all source notes in the table footer (cannot be used withtab_footnote()).
When using any of the location helper functions with an appropriate function
that has a locations argument (e.g., tab_style()), multiple locations
can be targeted by enclosing several cells_*() helper functions in a
list() (e.g., list(cells_body(), cells_grand_summary())).
Figures
Function ID
7-14
See also
Other Helper Functions:
adjust_luminance(),
cell_borders(),
cell_fill(),
cell_text(),
cells_body(),
cells_column_labels(),
cells_column_spanners(),
cells_footnotes(),
cells_grand_summary(),
cells_row_groups(),
cells_source_notes(),
cells_stub_grand_summary(),
cells_stubhead(),
cells_stub(),
cells_summary(),
cells_title(),
currency(),
default_fonts(),
escape_latex(),
google_font(),
gt_latex_dependencies(),
html(),
md(),
pct(),
px(),
random_id()
Examples
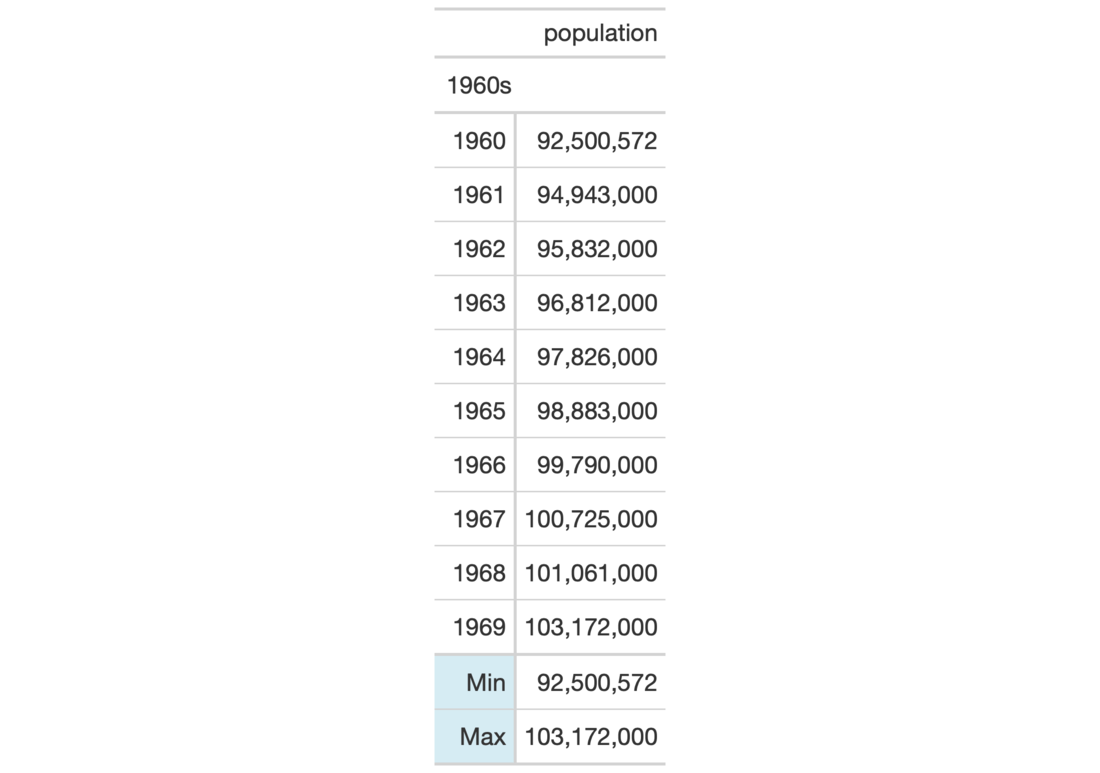
# Use `countrypops` to create a gt table; add # some styling to the summary data stub cells # with `tab_style()` and `cells_stub_summary()` tab_1 <- countrypops %>% dplyr::filter( country_name == "Japan", year < 1970) %>% dplyr::select(-contains("country")) %>% dplyr::mutate( decade = paste0(substr(year, 1, 3), "0s") ) %>% dplyr::group_by(decade) %>% gt( rowname_col = "year", groupname_col = "decade" ) %>% fmt_number( columns = population, decimals = 0 ) %>% summary_rows( groups = "1960s", columns = population, fns = list("min", "max"), formatter = fmt_number, decimals = 0 ) %>% tab_style( style = list( cell_text( weight = "bold", transform = "capitalize" ), cell_fill( color = "lightblue", alpha = 0.5 ) ), locations = cells_stub_summary( groups = "1960s" ) )